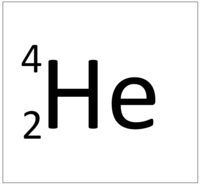Difference between revisions of "Relative Atomic Mass"
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Ar (relative atomic mass), page 167, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Ar (relative atomic mass), page 167, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Ar (relative atomic mass), page 23, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Ar (relative atomic mass), page 23, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Relative atomic mass (Ar), pages 4-5, 64, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d228 ''Relative atomic mass, A, pages 13, 21, 41, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10239 ''Relative atomic mass, A, pages 97, 123, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Relative atomic mass, pages 100-1, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Relative atomic mass, pages 120, 177, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Relative atomic mass, pages 26, 106, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Relative atomic mass, pages 26, 112, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Relative atomic mass, pages 62-63, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 16:04, 12 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
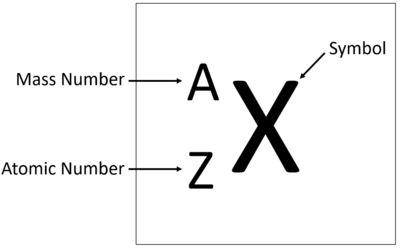
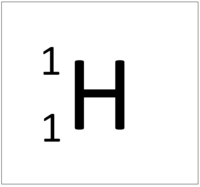
An element tile showing the mass number.
The Atomic Mass or mass number is the number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) in an atom.
About The Atomic Mass
- Two atoms of the same element may have the same Atomic Number but a different Atomic Mass depending on the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Elements with different mass numbers are called isotopes.
- The atomic mass is not affected by the number of electrons.
- Only the particles in the nucleus affect the atomic mass.
Examples
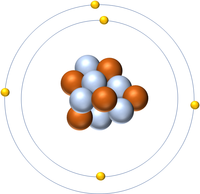
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has one nucleon so it has an atomic mass of 1. | Helium has four nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 4. | Lithium has seven nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 7. | Beryllium has nine nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 9. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning

An element tile showing the mass number.
The relative atomic mass or mass number of an element is the number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) in an atom.
The relative atomic mass in grams is also the mass of one mole or 6.02x1023 atoms of the element.
About Relative Atomic Mass
- The relative atomic mass in grams on the Periodic Table tells the mass of a mole of the element. A mole of the element is 6.02x1023 atoms of that element.
- Two atoms of the same element may have the same Atomic Number but a different Relative Atomic Mass depending on the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Elements with different mass numbers are called isotopes.
- The relative atomic mass is not affected by the number of electrons.
- Only the particles in the nucleus affect the relative atomic mass.
Examples
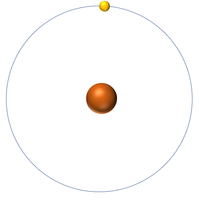
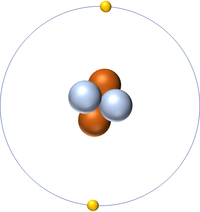
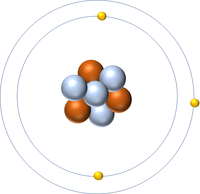
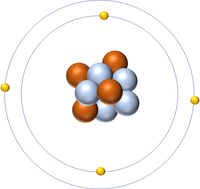
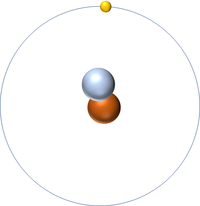
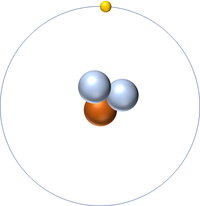
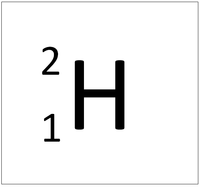
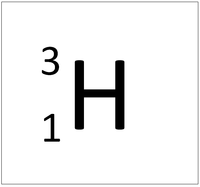
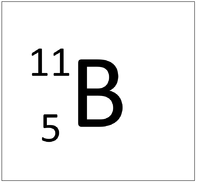
| Hydrogen | Deuterium | Tritium | Boron |
| Hydrogen has one nucleon so it has an atomic mass of 1 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Hydrogen have a mass of 1g. | Deuterium has two nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 2 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Deuterium have a mass of 2g. | Tritium has three nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 3 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Tritium have a mass of 3g. | Boron has eleven nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 11 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Boron have a mass of 11g. |
References
Edexcel
- Ar (relative atomic mass), page 167, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Ar (relative atomic mass), page 23, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
References
AQA
- Relative atomic mass (Ar), pages 4-5, 64, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, A, pages 13, 21, 41, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, A, pages 97, 123, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 100-1, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 120, 177, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 26, 106, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 26, 112, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 62-63, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA