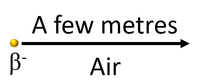Penetration Depth
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Penetration depth is how far into a material radiation can travel before being absorbed.
About Penetration Depth
- Penetration depth depends on the type of material and the type of radiation:
- Knowing the penetration depth in different materials is particularly important for ionising radiation to ensure that sources of ionising radiation can be handled safely.
Penetration Depth in Air
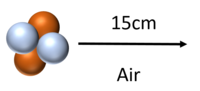
| Alpha particles can travel around 5cm through air (STP) before colliding with and ionising atoms or molecules. |
| Beta particles can travel several metres through air (STP) before colliding with and ionising atoms or molecules. |
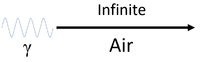
| Gamma-rays can travel an infinite distance through air and the chances of colliding with an atom or molecule are almost non-existent. |
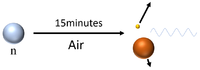
| Neutrons have a mean lifetime of around 15 minutes before they decay, so can travel several hundred kilometres depending on their velocity before they decay into a proton and a beta particle while emitting a gamma-ray. |
Penetration Depth Through Materials
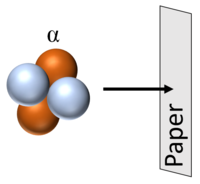
| Alpha particles can be stopped by a thin sheet of paper. |
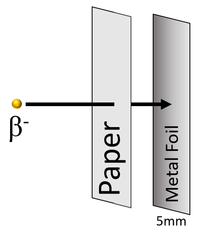
| Beta particles can penetrate paper but are stopped by around 5mm thickness of metal foil. |
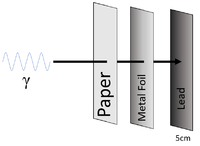
| Gamma-rays can penetrate paper and sheets of metal foil but cannot penetrate more than a few cm of Lead or a metre of concrete. |
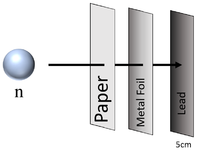
| Neutron radiation can penetrate paper and sheets of metal foil but cannot penetrate more than a few cm of Lead or a metre of concrete before they are captured by the nucleus of an atom. |