Difference between revisions of "Earth"
| (36 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The home [[planet]] of the [[Human]] [[species]]. | + | ==Key Stage 2== |
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | The [[Earth]] is the third [[planet]] form [[The Sun]] and the home [[planet]] of the [[Human]] [[species]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:Earth.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About The Earth=== | ||
| + | : The [[Earth]] is the only [[planet]] known to have living creatures on it. | ||
| + | : The [[Earth]] has one [[moon]] called [[The Moon]]. | ||
| + | : The [[Earth]] is just the right distance from [[The Sun]] for [[water]] to be a [[liquid]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | The [[Earth]] is the third [[planet]] form the [[The Sun]] and the home [[planet]] of the [[Human]] [[species]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Structure of the Earth=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:EarthStructure.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the layers of the [[Earth]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *[[Crust]]: The top layer of the [[Earth]] is called the [[Crust]]. It is made of [[rock]]s but two thirds is covered in a layer of [[water]]. | ||
| + | *[[Mantle]]: The layer under the [[Crust]] is called the [[Mantle]]. It is made of [[rock]] that is under such a high [[pressure]] that it behaves [[Plastic (Property)|plastically]]. | ||
| + | *[[Outer Core]]: The [[Outer Core]] is a [[liquid]] layer below the [[Mantle]]. | ||
| + | *[[Inner Core]]: Underneath the [[Outer Core]] is the [[Inner Core]] at the very centre of [[Earth]]. It is a [[solid]] [[sphere]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Crust==== | ||
| + | The [[Crust]] is split into several lumps that float on the [[Mantle]]. They are called [[Tectonic Plate]]s. They move around separately and and when the rub against each other this causes [[Earthquake]]s. If one [[Tectonic Plate]] moves on top of another the [[Tectonic Plate]] underneath starts to [[melt]] and [[magma]] rises up to make [[Volcano]]es. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:TectonicPlates.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the different [[Tectonic Plate]]s that make the [[Earth]]s [[Crust]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Composition of the Earth=== | ||
| + | The different layers of [[Earth]] are made of different materials. | ||
| + | *[[Crust]] - The most common chemical elements in the [[Crust]] are [[Oxygen]] (46.6%), [[Silicon]] (27.7%), [[Aluminium]] (8.1%), [[Iron]] (5.0%), [[Calcium]] (3.6%). | ||
| + | *[[Mantle]] - The [[Mantle]] is mostly made of Silicate [[rock]]s. | ||
| + | *[[Outer Core]] - The [[Outer Core]] is mostly made of [[liquid]] [[Iron]] and [[Nickel]]. | ||
| + | *[[Inner Core]] - The [[Inner Core]] is mostly made of [[solid]] [[Iron]] and [[Nickel]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Earth's Atmosphere=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:AtmosphericGases.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Pie Chart]] showing the percentage of different [[gas]]s in the '''Earth's Atmosphere'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | : The '''Earth's Atmosphere''' has not always had the same proportions of [[gas]]es. 3.9 billion [[year]]s ago there was no [[Oxygen]] in the [[atmosphere]]. In the last 200 years humans have caused the [[Carbon Dioxide]] in the '''Earth's Atmosphere''' to double. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Earth's Resources=== | ||
| + | : '''Earth's''' resources are the parts of the [[Earth]] that [[human]]s can use to survive, build technology and provide power. | ||
| + | : The resources on Earth are limited. Which means they can run out if we use them all. This means it's important to [[recycling|recycle]] our resources. | ||
| + | : The resources humans need to survive are; fresh water, food and building materials. For this we need unpolluted rivers, land to grow crops and [[tree]]s and [[rock]]s to build our homes. | ||
| + | : The resources humans need to build technology are; [[metal]] [[ore]]s and [[Crude Oil|crude oil]]. | ||
| + | : The resources humans need to provide power are; [[Crude Oil|crude oil]], [[coal]], [[Natural Gas|natural gas]], [[Nuclear Fuel|nuclear fuel]], [[biofuel]], [[Solar Power|sunlight]], [[Wind Power|wind]], [[Hydroelectric Power|river]]s, [[Tidal Power|tides]], [[Wave Power|waves]] and [[Geothermal Power|geothermal vents]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Earth's Magnetic Field=== | ||
| + | : The core of the [[Earth]] spins at a different speed to the rest of the [[planet]] and this causes a [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. | ||
| + | : The [[Earth]]'s [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] helps protect the [[planet]] against Solar Flares from [[The Sun]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |[[File:MagneticFieldLinesEarth.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:MagneticFieldEarth.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows the direction of [[Earth]]'s [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] of [[Earth]] appears as if there were a giant [[Bar Magnet|bar magnet]] inside the [[Earth]]. The North of [[Earth]] is the [[Poles|South Seeking Pole]] of a [[magnet]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | The [[Earth]] is the third [[planet]] form the [[The Sun]] and the home [[planet]] of the [[Human]] [[species]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Structure of the Earth=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:EarthStructure.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the layers of the [[Earth]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *[[Crust]]: The top layer of the [[Earth]] is called the [[Crust]]. It is made of [[rock]]s but two thirds is covered in a layer of [[water]]. | ||
| + | *[[Mantle]]: The layer under the [[Crust]] is called the [[Mantle]]. It is made of [[rock]] that is under such a high [[pressure]] that it behaves [[Plastic (Property)|plastically]]. | ||
| + | *[[Outer Core]]: The [[Outer Core]] is a [[liquid]] layer below the [[Mantle]]. | ||
| + | *[[Inner Core]]: Underneath the [[Outer Core]] is the [[Inner Core]] at the very centre of [[Earth]]. It is a [[solid]] [[sphere]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Crust==== | ||
| + | The [[Crust]] is split into several lumps that float on the [[Mantle]]. They are called [[Tectonic Plate]]s. They move around separately and and when the rub against each other this causes [[Earthquake]]s. If one [[Tectonic Plate]] moves on top of another the [[Tectonic Plate]] underneath starts to [[melt]] and [[magma]] rises up to make [[Volcano]]es. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:TectonicPlates.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the different [[Tectonic Plate]]s that make the [[Earth]]s [[Crust]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Composition of the Earth=== | ||
| + | The different layers of [[Earth]] are made of different materials. | ||
| + | *[[Crust]] - The most common chemical elements in the [[Crust]] are [[Oxygen]] (46.6%), [[Silicon]] (27.7%), [[Aluminium]] (8.1%), [[Iron]] (5.0%), [[Calcium]] (3.6%). | ||
| + | *[[Mantle]] - The [[Mantle]] is mostly made of [[Silicate]] [[rock]]s. | ||
| + | *[[Outer Core]] - The [[Outer Core]] is mostly made of [[liquid]] [[Iron]] and [[Nickel]]. | ||
| + | *[[Inner Core]] - The [[Inner Core]] is mostly made of [[solid]] [[Iron]] and [[Nickel]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Earth's Atmosphere=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:AtmosphericGases.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Pie Chart]] showing the percentage of different [[gas]]s in the '''Earth's Atmosphere'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | : The '''Earth's Atmosphere''' has not always had the same proportions of [[gas]]es. 3.9 billion [[year]]s ago there was no [[Oxygen]] in the [[atmosphere]]. In the last 200 years humans have caused the [[Carbon Dioxide]] in the '''Earth's Atmosphere''' to double. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Earth's Resources=== | ||
| + | : '''Earth's''' resources are the parts of the [[Earth]] that [[human]]s can use to survive, build technology and provide power. | ||
| + | : The resources on Earth are limited. Which means they can run out if we use them all. This means it's important to [[recycling|recycle]] our resources. | ||
| + | : The resources humans need to survive are; fresh water, food and building materials. For this we need unpolluted rivers, land to grow crops and [[tree]]s and [[rock]]s to build our homes. | ||
| + | : The resources humans need to build technology are; [[metal]] [[ore]]s and [[Crude Oil|crude oil]]. | ||
| + | : The resources humans need to provide power are; [[Crude Oil|crude oil]], [[coal]], [[Natural Gas|natural gas]], [[Nuclear Fuel|nuclear fuel]], [[biofuel]], [[Solar Power|sunlight]], [[Wind Power|wind]], [[Hydroelectric Power|river]]s, [[Tidal Power|tides]], [[Wave Power|waves]] and [[Geothermal Power|geothermal vents]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Earth's Magnetic Field=== | ||
| + | : The core of the [[Earth]] spins at a different speed to the rest of the [[planet]] and this causes a [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. | ||
| + | : The [[Earth]]'s [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] helps protect the [[planet]] against Solar Flares from [[The Sun]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |[[File:MagneticFieldLinesEarth.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:MagneticFieldEarth.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows the direction of [[Earth]]'s [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] of [[Earth]] appears as if there were a giant [[Bar Magnet|bar magnet]] inside the [[Earth]]. The North of [[Earth]] is the [[Poles|South Seeking Pole]] of a [[magnet]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Earth, pages 248, 249, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Earth, pages 274-9, 290, 292, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Earth, pages 28-29, 186-187, 233, 236-237, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Earth; magnetic field, page 223, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Earth; magnetic field, page 290, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Earth; orbit of, pages 253-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Earth; structure, page 211, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Earth; structure, pages 285, 286, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Earth; temperature of, pages, 211-12, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Earth; temperature; pages 258, 259, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Earth`s magnetic field, pages 277, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Earth’s magnetic field, page 217, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac103 ''Earth’s structure, page 90, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac104 ''Earth’s temperature, page 87, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Earth; Atmosphere, pages 38-39, 243, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Earth; Energy source, pages 226-227, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Earth; Gravitational force, pages 82, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Earth; Magnetic field, pages 120-121, 123, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Earth; Satellites, pages 240, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Earth; Structure of, pages 244-245, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Beyond the Curriculum== | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HCDVN7DCzYE}} | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JGXi_9A__Vc}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:32, 5 December 2019
Key Stage 2
Meaning
The Earth is the third planet form The Sun and the home planet of the Human species.
About The Earth
- The Earth is the only planet known to have living creatures on it.
- The Earth has one moon called The Moon.
- The Earth is just the right distance from The Sun for water to be a liquid.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The Earth is the third planet form the The Sun and the home planet of the Human species.
Structure of the Earth
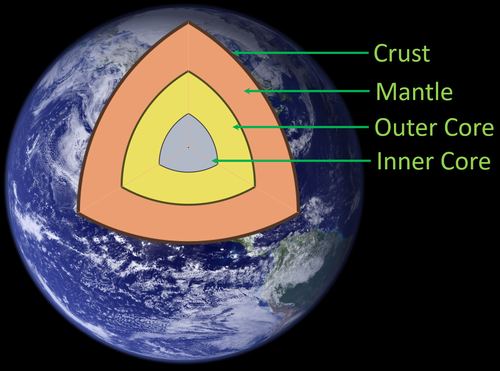
| A diagram showing the layers of the Earth. |
- Crust: The top layer of the Earth is called the Crust. It is made of rocks but two thirds is covered in a layer of water.
- Mantle: The layer under the Crust is called the Mantle. It is made of rock that is under such a high pressure that it behaves plastically.
- Outer Core: The Outer Core is a liquid layer below the Mantle.
- Inner Core: Underneath the Outer Core is the Inner Core at the very centre of Earth. It is a solid sphere.
Crust
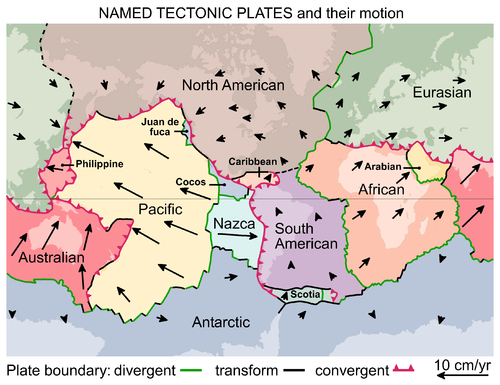
The Crust is split into several lumps that float on the Mantle. They are called Tectonic Plates. They move around separately and and when the rub against each other this causes Earthquakes. If one Tectonic Plate moves on top of another the Tectonic Plate underneath starts to melt and magma rises up to make Volcanoes.
| A diagram showing the different Tectonic Plates that make the Earths Crust. |
Composition of the Earth
The different layers of Earth are made of different materials.
- Crust - The most common chemical elements in the Crust are Oxygen (46.6%), Silicon (27.7%), Aluminium (8.1%), Iron (5.0%), Calcium (3.6%).
- Mantle - The Mantle is mostly made of Silicate rocks.
- Outer Core - The Outer Core is mostly made of liquid Iron and Nickel.
- Inner Core - The Inner Core is mostly made of solid Iron and Nickel.
Earth's Atmosphere
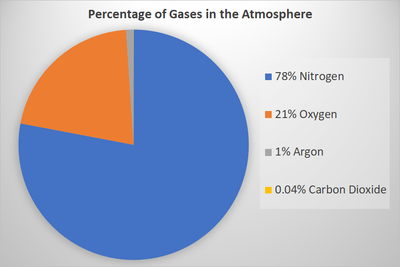
| A Pie Chart showing the percentage of different gass in the Earth's Atmosphere. |
- The Earth's Atmosphere has not always had the same proportions of gases. 3.9 billion years ago there was no Oxygen in the atmosphere. In the last 200 years humans have caused the Carbon Dioxide in the Earth's Atmosphere to double.
Earth's Resources
- Earth's resources are the parts of the Earth that humans can use to survive, build technology and provide power.
- The resources on Earth are limited. Which means they can run out if we use them all. This means it's important to recycle our resources.
- The resources humans need to survive are; fresh water, food and building materials. For this we need unpolluted rivers, land to grow crops and trees and rocks to build our homes.
- The resources humans need to build technology are; metal ores and crude oil.
- The resources humans need to provide power are; crude oil, coal, natural gas, nuclear fuel, biofuel, sunlight, wind, rivers, tides, waves and geothermal vents.
Earth's Magnetic Field
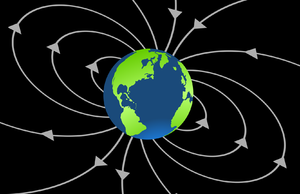
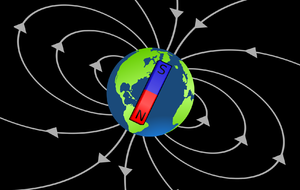
- The core of the Earth spins at a different speed to the rest of the planet and this causes a magnetic field.
- The Earth's magnetic field helps protect the planet against Solar Flares from The Sun.
| This diagram shows the direction of Earth's magnetic field. | The magnetic field of Earth appears as if there were a giant bar magnet inside the Earth. The North of Earth is the South Seeking Pole of a magnet. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Earth is the third planet form the The Sun and the home planet of the Human species.
Structure of the Earth
| A diagram showing the layers of the Earth. |
- Crust: The top layer of the Earth is called the Crust. It is made of rocks but two thirds is covered in a layer of water.
- Mantle: The layer under the Crust is called the Mantle. It is made of rock that is under such a high pressure that it behaves plastically.
- Outer Core: The Outer Core is a liquid layer below the Mantle.
- Inner Core: Underneath the Outer Core is the Inner Core at the very centre of Earth. It is a solid sphere.
Crust
The Crust is split into several lumps that float on the Mantle. They are called Tectonic Plates. They move around separately and and when the rub against each other this causes Earthquakes. If one Tectonic Plate moves on top of another the Tectonic Plate underneath starts to melt and magma rises up to make Volcanoes.
| A diagram showing the different Tectonic Plates that make the Earths Crust. |
Composition of the Earth
The different layers of Earth are made of different materials.
- Crust - The most common chemical elements in the Crust are Oxygen (46.6%), Silicon (27.7%), Aluminium (8.1%), Iron (5.0%), Calcium (3.6%).
- Mantle - The Mantle is mostly made of Silicate rocks.
- Outer Core - The Outer Core is mostly made of liquid Iron and Nickel.
- Inner Core - The Inner Core is mostly made of solid Iron and Nickel.
Earth's Atmosphere
| A Pie Chart showing the percentage of different gass in the Earth's Atmosphere. |
- The Earth's Atmosphere has not always had the same proportions of gases. 3.9 billion years ago there was no Oxygen in the atmosphere. In the last 200 years humans have caused the Carbon Dioxide in the Earth's Atmosphere to double.
Earth's Resources
- Earth's resources are the parts of the Earth that humans can use to survive, build technology and provide power.
- The resources on Earth are limited. Which means they can run out if we use them all. This means it's important to recycle our resources.
- The resources humans need to survive are; fresh water, food and building materials. For this we need unpolluted rivers, land to grow crops and trees and rocks to build our homes.
- The resources humans need to build technology are; metal ores and crude oil.
- The resources humans need to provide power are; crude oil, coal, natural gas, nuclear fuel, biofuel, sunlight, wind, rivers, tides, waves and geothermal vents.
Earth's Magnetic Field
- The core of the Earth spins at a different speed to the rest of the planet and this causes a magnetic field.
- The Earth's magnetic field helps protect the planet against Solar Flares from The Sun.
| This diagram shows the direction of Earth's magnetic field. | The magnetic field of Earth appears as if there were a giant bar magnet inside the Earth. The North of Earth is the South Seeking Pole of a magnet. |
References
AQA
- Earth, pages 248, 249, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Earth, pages 274-9, 290, 292, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Earth, pages 28-29, 186-187, 233, 236-237, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Earth; magnetic field, page 223, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Earth; magnetic field, page 290, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Earth; orbit of, pages 253-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Earth; structure, page 211, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Earth; structure, pages 285, 286, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Earth; temperature of, pages, 211-12, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Earth; temperature; pages 258, 259, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Earth`s magnetic field, pages 277, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Earth’s magnetic field, page 217, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Earth’s structure, page 90, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Earth’s temperature, page 87, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
OCR
- Earth; Atmosphere, pages 38-39, 243, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Earth; Energy source, pages 226-227, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Earth; Gravitational force, pages 82, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Earth; Magnetic field, pages 120-121, 123, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Earth; Satellites, pages 240, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Earth; Structure of, pages 244-245, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR