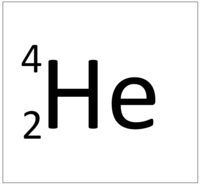Difference between revisions of "Helium"
| (20 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Helium]] is a [[gas]]. | [[Helium]] is a [[gas]]. | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | [[File:HeliumSymbol1.png|right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Helium]].]] | ||
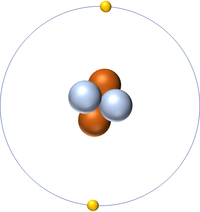
| + | [[File:He-4_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of a [[Helium]] [[atom]] with 2 [[proton]]s and 2 [[neutron]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 2 [[electron]]s orbiting the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Helium]] is a [[Group 0]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 2. |
| − | [[ | + | |
===About Helium=== | ===About Helium=== | ||
: [[Helium]] has the [[Chemical Formula|chemical formula]] [[Helium|He]]. | : [[Helium]] has the [[Chemical Formula|chemical formula]] [[Helium|He]]. | ||
| − | : [[Helium]] is [[ | + | : [[Helium]] has two [[proton]]s and two [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Atomic Number]] of 2 and an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 4. |
| + | : [[Helium]] is a [[Noble Gas]]. | ||
: [[Helium]] is a [[gas]] at [[STP|room temperature]]. | : [[Helium]] is a [[gas]] at [[STP|room temperature]]. | ||
: [[Helium]] [[gas]] is less [[density|dense]] than [[air]]. | : [[Helium]] [[gas]] is less [[density|dense]] than [[air]]. | ||
| − | : An [[atom]] of [[Helium]] has two [[electron]]s | + | : An [[atom]] of [[Helium]] has a full [[Outer Shell|outer shell]] of two [[electron]]s so it is [[inert]]. |
| + | |||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | [[File:HeKS4.png|right|200px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Helium]].]] | ||
| + | [[File:He-4_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of the [[Bohr Model]] of a [[Helium]]-4 [[isotope]] with 2 [[proton]]s and 2 [[neutron]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 2 [[electron]]s in its [[Outer Shell|outer shell]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Helium]] is a [[ | + | [[Helium]] is a [[Group 0]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 2 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. |
| + | |||
===About Helium=== | ===About Helium=== | ||
: [[Helium]] has the [[Chemical Formula|chemical formula]] [[Helium|He]]. | : [[Helium]] has the [[Chemical Formula|chemical formula]] [[Helium|He]]. | ||
| − | : [[Helium]] is [[ | + | : The most [[Stable Isotope|stable isotope]] of [[Helium]] has two [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 4. |
| + | : [[Helium]] is a [[Noble Gas]]. | ||
: [[Helium]] is a [[gas]] at [[STP|standard temperature and pressure]]. | : [[Helium]] is a [[gas]] at [[STP|standard temperature and pressure]]. | ||
: [[Helium]] [[gas]] is less [[density|dense]] than [[air]]. | : [[Helium]] [[gas]] is less [[density|dense]] than [[air]]. | ||
| − | : An [[atom]] of [[Helium]] has two [[electron]]s | + | : An [[atom]] of [[Helium]] has a full [[Outer Shell|outer shell]] of two [[electron]]s so it is [[inert]]. |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |[[File:Helium.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:HeliumSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" colspan = "2"|[[Helium]] always has 2 [[proton]]s. The most [[Stable Isotope|stable]] [[isotope]] has 2 [[neutron]]s. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Beyond the Curriculum== | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hLUcO26Q7wE}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Helium, page 106, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Helium, pages 109, 111-12, 130-1, 280-1, 283-4, 286-7, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:50, 19 February 2021
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
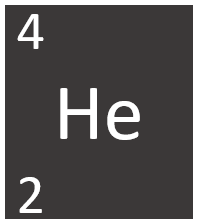
Helium is a Group 0 element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 2.
About Helium
- Helium has the chemical formula He.
- Helium has two protons and two neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 2 and an atomic mass of 4.
- Helium is a Noble Gas.
- Helium is a gas at room temperature.
- Helium gas is less dense than air.
- An atom of Helium has a full outer shell of two electrons so it is inert.
Key Stage 4
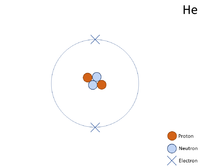
A 2 dimensional representation of the Bohr Model of a Helium-4 isotope with 2 protons and 2 neutrons in the nucleus and 2 electrons in its outer shell.
Meaning
Helium is a Group 0 element, on the Periodic Table, with 2 protons in the nucleus.
About Helium
- Helium has the chemical formula He.
- The most stable isotope of Helium has two neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 4.
- Helium is a Noble Gas.
- Helium is a gas at standard temperature and pressure.
- Helium gas is less dense than air.
- An atom of Helium has a full outer shell of two electrons so it is inert.
| Helium always has 2 protons. The most stable isotope has 2 neutrons. | |