Difference between revisions of "State Change"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 2== ===Meaning=== A '''state change''' is when a material changes from one state of matter to another. ===About State Changes=== : A state...") |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
*[[Evaporating]] is when a liquid turns into a gas. | *[[Evaporating]] is when a liquid turns into a gas. | ||
*[[Condensing]] is when a gas turns into a liquid. | *[[Condensing]] is when a gas turns into a liquid. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[File:ParticleModelStateChanges.png|right|300px|thumb|This diagram shows the '''changes of state''' between the three [[State of Matter|states of matter]].]] | ||
| + | A '''state change''' is when a [[substance]] changes from one [[State of Matter|state of matter]] to another. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About State Changes=== | ||
| + | : A [[State of Matter|state of matter]] can change if the [[temperature]] changes. | ||
| + | *[[Melting]] is when [[solid]] turns into a [[liquid]]. | ||
| + | *[[Freezing]] is when a [[liquid]] turns into a [[solid]]. | ||
| + | *[[Evaporating]] is when a [[liquid]] turns into a [[gas]]. | ||
| + | *[[Condensing]] is when a [[gas]] turns into a [[liquid]]. | ||
| + | *[[Subliming]] is when a [[solid]] turns into a [[gas]]. | ||
| + | *[[Depositing]] is when a [[gas]] turns into a [[solid]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Energy and State Changes=== | ||
| + | : '''Changing state''' either needs [[energy]] to happen or releases stored [[energy]] when it happens. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
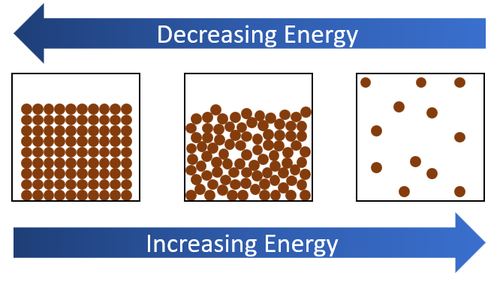
| + | |[[File:EnergyStateChanges.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |When [[energy]] is added by [[heat]]ing a [[solid]] will turn into a [[liquid]] and then a [[liquid]] will turn into a [[gas]]. When [[energy]] is taken away by cooling a [[gas]] will turn into a [[liquid]] and a [[liquid]] will turn into a [[solid]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Melting]], [[Evaporating]] and [[Subliming]] are [[endothermic]] changes because they need [[energy]] to happen. The [[material]] has more [[energy]] at the end than it did the beginning. | ||
| + | : When a [[solid]] [[melting|melts]] [[energy]] is needed to break the [[bond]]s holding the [[particle]]s in fixed positions. | ||
| + | : When a [[liquid]] [[evaporating|evaporates]] [[energy]] is needed to break the [[bond]]s that keep the [[particle]]s together. | ||
| + | : When a [[solid]] [[subliming|sublimates]] [[energy]] is needed to break the [[bond]]s holding the [[particle]]s in fixed positions and keeping the [[particle]]s together. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Freezing]], [[Condensing]] and [[Depositing]] are [[exothermic]] changes because it releases [[energy]] when it happens. The [[material]] has less after it has happened. | ||
| + | : When a [[gas]] [[condensing|condenses]] [[energy]] is released as [[bond]]s form between adjacent [[molecule]]s to hold them together. | ||
| + | : When a [[liquid]] [[freezing|freezes]] [[energy]] is released as [[bond]]s form between adjacent [[molecule]]s to keep them in fixed positions. | ||
| + | : When a [[gas]] [[depositing|deposits]] [[energy]] is released as [[bond]]s form between adjacent [[molecule]]s to hold them together and keep them in fixed positions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : When [[human]]s [[sweat]] the [[water]] [[evaporation|evaporates]] from the [[skin]] helping them cool down. This works because [[evaporation]] is an [[endothermic]] process so the [[sweat]] takes [[energy]] away from the [[skin]] when it [[evaporation|evaporates]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | A '''state change''' is a [[Physical Change|physical change]] in which a [[substance]] turns from one [[State of Matter|state of matter]] into to another. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About State Changes=== | ||
| + | : '''State changes''' are [[reversible]] because after a '''state change''' the [[material]] can be returned to its original form with the same [[property|properties]] as it started with. | ||
| + | : '''State changes''' happen when a [[substance]] gains enough [[energy]] to break the [[bond]]s holding [[particle]]s together or loses enough [[energy]] for [[bond]]s to form between [[particle]]s. | ||
| + | : When the [[bond]]s between [[particle]]s in a [[solid]] or a [[liquid]] are broken the [[particle]]s gain [[Potential Energy|potential energy]]. This is an [[endothermic]] process because it needs [[energy]]. | ||
| + | : When [[bond]]s are formed between [[particle]]s in a [[gas]] or a [[liquid]] the [[particle]]s lose [[Potential Energy|potential energy]]. This is an [[exothermic]] process because [[energy]] is given off. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''State changes, page 3, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:24, 29 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A state change is when a material changes from one state of matter to another.
About State Changes
- A state of matter can change if the temperature changes.
- Melting is when solid turns into a liquid.
- Freezing is when a liquid turns into a solid.
- Evaporating is when a liquid turns into a gas.
- Condensing is when a gas turns into a liquid.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
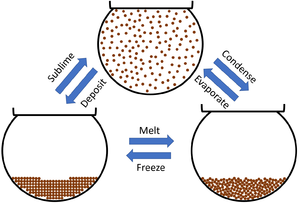
This diagram shows the changes of state between the three states of matter.
A state change is when a substance changes from one state of matter to another.
About State Changes
- A state of matter can change if the temperature changes.
- Melting is when solid turns into a liquid.
- Freezing is when a liquid turns into a solid.
- Evaporating is when a liquid turns into a gas.
- Condensing is when a gas turns into a liquid.
- Subliming is when a solid turns into a gas.
- Depositing is when a gas turns into a solid.
Energy and State Changes
| When energy is added by heating a solid will turn into a liquid and then a liquid will turn into a gas. When energy is taken away by cooling a gas will turn into a liquid and a liquid will turn into a solid. |
- Melting, Evaporating and Subliming are endothermic changes because they need energy to happen. The material has more energy at the end than it did the beginning.
- When a solid melts energy is needed to break the bonds holding the particles in fixed positions.
- When a liquid evaporates energy is needed to break the bonds that keep the particles together.
- When a solid sublimates energy is needed to break the bonds holding the particles in fixed positions and keeping the particles together.
- Freezing, Condensing and Depositing are exothermic changes because it releases energy when it happens. The material has less after it has happened.
- When a gas condenses energy is released as bonds form between adjacent molecules to hold them together.
- When a liquid freezes energy is released as bonds form between adjacent molecules to keep them in fixed positions.
- When a gas deposits energy is released as bonds form between adjacent molecules to hold them together and keep them in fixed positions.
- When humans sweat the water evaporates from the skin helping them cool down. This works because evaporation is an endothermic process so the sweat takes energy away from the skin when it evaporates.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A state change is a physical change in which a substance turns from one state of matter into to another.
About State Changes
- State changes are reversible because after a state change the material can be returned to its original form with the same properties as it started with.
- State changes happen when a substance gains enough energy to break the bonds holding particles together or loses enough energy for bonds to form between particles.
- When the bonds between particles in a solid or a liquid are broken the particles gain potential energy. This is an endothermic process because it needs energy.
- When bonds are formed between particles in a gas or a liquid the particles lose potential energy. This is an exothermic process because energy is given off.