Difference between revisions of "State of Matter"
(→About States of Matter) |
(→Key Stage 4) |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
: [[Material|Materials]] can be [[solid]], [[liquid]] or [[gas]]. | : [[Material|Materials]] can be [[solid]], [[liquid]] or [[gas]]. | ||
: The '''state of matter''' can be altered by changing the [[temperature]] of the [[material]] or changing the [[pressure]] on the [[material]]. | : The '''state of matter''' can be altered by changing the [[temperature]] of the [[material]] or changing the [[pressure]] on the [[material]]. | ||
| − | + | : The [[property|properties]] of [[solid]]s, [[liquid]]s and [[gas]]es can be explained by the way the [[particle]]s inside those [[substance]]s behave. | |
| − | : | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 142: | Line 135: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Thermal Conduction]] is very poor in a [[gas]]es. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Thermal Conduction]] is very poor in a [[gas]]es. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Why isn't everything a gas?==== | ||
| + | : When [[particle]]s are near each other, they tend to stick together. This is due to [[force]]s acting between [[adjacent]] [[particle]]s. When two [[particle]]s are near one another they are [[attracted]] together. This causes those [[particle]]s to come together. Without this [[force]] of [[attraction]] between particles they would not stick together and there would be no [[solid]] or [[liquid]] '''states'''. | ||
| + | : What determines if a [[substance]] is a [[solid]], [[liquid]] or [[gas]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]] is how big that [[force]] of [[attraction]] is. | ||
| + | ====Why Solids and Liquids exist==== | ||
| + | : Different [[substance]]s have a different [[force]] of [[attraction]] between the [[adjacent]] [[particle]]s. | ||
| + | : Silicon dioxide (sand and glass) is [[solid]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]] because there is a strong [[force]] of [[attraction]] between [[adjacent]] [[molecule]]s. | ||
| + | : [[Water]] is a [[liquid]] at [[room temperature]] because the [[force]] of [[attraction]] is not great enough to hold the [[molecule]]s in position. However, it is great enough to keep them together. | ||
| + | : [[Oxygen]] is a gas at [[room temperature]] because there is a very weak [[force]] of [[attraction]] between [[adjacent]] [[molecules]]. | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 23 December 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
State of matter means whether a material is solid, liquid or gas.
About States of Matter
- Materials can be solid, liquid or gas.
- The state of matter can be changed by heating or cooling the material.
- Heating can turn a solid into a liquid. This is called melting.
- Heating can turn a liquid to a gas. This is called evaporating.
- Cooling can turn a gas into a liquid. This is called condensing.
- Cooling can turn a liquid into solid. This is called freezing.
| Brick is a solid material. | Water is a liquid material. | Inside the balloon is a gas called helium. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
State of matter means whether a material is solid, liquid or gas.
About States of Matter
- Materials can be solid, liquid or gas.
- The state of matter can be changed by heating or cooling the material.
- Heating can turn a solid into a liquid by melting or it can turn a solid straight into a gas by subliming.
- Heating can turn a liquid to a gas. This is called evaporating.
- Cooling can turn a gas into a liquid by condensing or it can turn a gas into a solid by depositing.
- Cooling can turn a liquid into solid. This is called freezing.
| This diagram shows the 3 states of matter in the particle model. |
Properties of the States of Matter
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| Cannot be compressed. | Cannot be compressed. | Can be compressed. |
| Does not flow. | Can flow. | Can flow. |
| Holds its shape. | Fits the shape of the container. | Fits the size and shape of the container. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
State of matter means whether a material is solid, liquid or gas.
About States of Matter
- Materials can be solid, liquid or gas.
- The state of matter can be altered by changing the temperature of the material or changing the pressure on the material.
- The properties of solids, liquids and gases can be explained by the way the particles inside those substances behave.
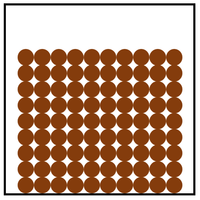
| Particle Diagram | Particle Arrangement | Property |
| Particles are in fixed positions. | Solids hold their shape. | |
| Convection cannot happen in solids. | ||
| Particles are very close together. | Solids cannot be compressed. | |
| Sound passes through solids faster than liquids and gases. | ||
| Particles vibrate. | ||
| Thermal Conduction happens best in solids. |
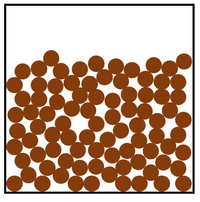
| Particle Diagram | Particle Arrangement | Property |
| Particles can slide past each other. | Liquids can be poured. | |
| Liquids fit the shape of their container. | ||
| Convection happens in solids. | ||
| Particles and close together. | Liquids cannot be compressed. | |
| Sound passes through liquids faster than gases. | ||
| Thermal Conduction happens in liquids but not as well as in solids. |
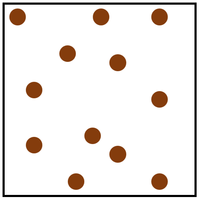
| Particle Diagram | Particle Arrangement | Property |
| Particles are free to move in all directions. | Gases fit the size of their container. | |
| Gases fit the shape of their container. | ||
| Convection happens most easily in gases. | ||
| Particles are spread apart. | Gases can be compressed into a smaller volume. | |
| Sound passes through gases slower than liquids and solids. | ||
| Thermal Conduction is very poor in a gases. |
Why isn't everything a gas?
- When particles are near each other, they tend to stick together. This is due to forces acting between adjacent particles. When two particles are near one another they are attracted together. This causes those particles to come together. Without this force of attraction between particles they would not stick together and there would be no solid or liquid states.
- What determines if a substance is a solid, liquid or gas at room temperature is how big that force of attraction is.
Why Solids and Liquids exist
- Different substances have a different force of attraction between the adjacent particles.
- Silicon dioxide (sand and glass) is solid at room temperature because there is a strong force of attraction between adjacent molecules.
- Water is a liquid at room temperature because the force of attraction is not great enough to hold the molecules in position. However, it is great enough to keep them together.
- Oxygen is a gas at room temperature because there is a very weak force of attraction between adjacent molecules.