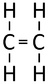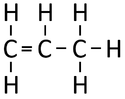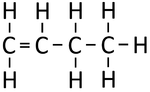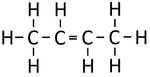Difference between revisions of "Alkene"
(→Key Stage 4) |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Alkene]]s are [[hydrocarbon]] [[compound]]s with one [[Double Bond|double bond]] and the [[General Formula | + | [[Alkene]]s are [[hydrocarbon]] [[compound]]s with one [[Double Bond|double bond]] and the [[General Formula|general formula]]; C<sub>n</sub>H<sub>2n</sub> |
===About Alkenes=== | ===About Alkenes=== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: The [[Functional Group|functional group]] of the [[Alkene]]s is the [[Double Bond|double bonds]] between the [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s. | : The [[Functional Group|functional group]] of the [[Alkene]]s is the [[Double Bond|double bonds]] between the [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s. | ||
: [[Alkene]]s are long chains of [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s [[Covalent Bond|covalently bonded]] together with [[Double Bond|double]] and [[Single Bond|single bonds]] and [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s taking the remaining [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | : [[Alkene]]s are long chains of [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s [[Covalent Bond|covalently bonded]] together with [[Double Bond|double]] and [[Single Bond|single bonds]] and [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s taking the remaining [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | ||
| + | : [[Alkene]]s are referred to as [[Unsaturated Hydrocarbon|unsaturated hydrocarbons]] because the [[Double Bond|double bond]] means it is not [[Saturated Hydrocarbon|saturated]] (full) with [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s. | ||
| + | : [[Alkene Test|Testing for '''alkenes''']] can be done by adding them to [[Bromine Water]]. If the [[Bromine Water]] turns from orange to colourless, then an [[alkene]] is present. During this test the [[Bromine]] [[Chemical Reaction|react]]s with the [[alkene]] to form a [[Bromoalkane]]. | ||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Bromine]] → [[Dibromoethane]] | ||
| + | <math>C_2H_4 + Br_2 → C_2H_4Br_2</math> | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" | |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Ethene''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Propene |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''But-1-ene''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''But-2-ene''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Chemical Formula]] (C<sub>n</sub>H<sub>2n</sub>) |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>6</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Structural Formula]] |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>2</sub>CHCH<sub>3</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>2</sub>CHCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>CHCHCH<sub>3</sub> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Structural Diagram]] |
|[[File:StructuralDiagramEthene.png|center|50px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramEthene.png|center|50px]] | ||
| − | |[[File:StructuralDiagramPropene.png|center| | + | |[[File:StructuralDiagramPropene.png|center|125px]] |
|[[File:StructuralDiagramBut-1-ene.png|center|150px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramBut-1-ene.png|center|150px]] | ||
|[[File:StructuralDiagramBut-2-ene.png|center|150px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramBut-2-ene.png|center|150px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
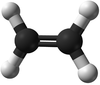
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Ball and Stick Model]] |
| − | |[[File:BallandStickEthene.png|center| | + | |[[File:BallandStickEthene.png|center|100px]] |
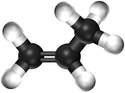
| − | |[[File:BallandStickPropene.png|center| | + | |[[File:BallandStickPropene.png|center|125px]] |
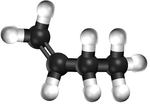
|[[File:BallandStickBut-1-ene.png|center|150px]] | |[[File:BallandStickBut-1-ene.png|center|150px]] | ||
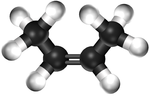
|[[File:BallandStickBut-2-ene.png|center|150px]] | |[[File:BallandStickBut-2-ene.png|center|150px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Reactions of Alkenes=== | ||
| + | ====Combustion==== | ||
| + | During [[combustion]] of [[alkene]]s the [[Carbon]] and [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s are [[oxidised]] to produce [[Carbon Dioxide]] and [[Water]]. | ||
| + | =====Complete Combustion===== | ||
| + | [[Complete Combustion|Complete combustion]] occurs when there is enough [[Oxygen]] to completely [[Oxidise]] all of the [[atom]]s in the [[alkene]]. | ||
| + | In the [[Complete Combustion|complete combustion]] of [[alkene]]s the only [[product]]s are [[Carbon Dioxide]] and [[Water]]. | ||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Dioxide]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub> + 3O<sub>2</sub> → 2CO<sub>2</sub> + 2H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Propene]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Dioxide]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | : 2C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>6</sub> + 9O<sub>2</sub> → 6CO<sub>2</sub> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Butene]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Dioxide]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub> + 6O<sub>2</sub> → 4CO<sub>2</sub> + 4H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Incomplete Combustion===== | ||
| + | [[Incomplete Combustion|Incomplete combustion]] occurs when there is not enough [[Oxygen]] to [[Oxidise]] all of the [[atom]]s in the [[alkene]]. | ||
| + | During [[Incomplete Combustion|incomplete combustion]] of [[alkene]]s the [[product]]s may include [[Carbon]] ([[soot]]) and [[Carbon Monoxide]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Soot]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub> + O<sub>2</sub> → 2C + 2H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Monoxide]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub> + 2O<sub>2</sub> → 2CO + 2H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Soot]] + [[Carbon Monoxide]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | : 2C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub> + 3O<sub>2</sub> → 2C + 2CO + 4H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Reaction with Halogens==== | ||
| + | When [[halogen]]s are added to [[alkene]]s the [[Double Bond|double bond]] in the [[alkene]]s breaks and the [[halogen]]s [[bond]] in its place. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Chlorine]] → Dichloroethane | ||
| + | : C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub> + Cl<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Propene]] + [[Bromine]] → Dibromopropane | ||
| + | : C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>6</sub> + Br<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>6</sub>Br<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Butene]] + [[Iodine]] → Diiodobutane | ||
| + | : C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub> + I<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub>I<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Reaction with Hydrogen==== | ||
| + | [[Alkene]]s can be [[Saturated Hydrocarbon|saturated]] with extra [[Hydrogen]] using a [[catalyst]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Hydrogen]] → [[Ethane]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub> + H<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>6</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Propene]] + [[Hydrogen]] → [[Propane]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>6</sub> + H<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>8</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Butene]] + [[Hydrogen]] → [[Butane]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub> + H<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>10</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Reaction with Steam==== | ||
| + | [[Alkene]]s can [[Chemical Reaction|react]] with [[steam]] to [[product|produce]] [[alcohol]]s using a [[catalyst]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethene]] + [[Steam]] ⇌ [[Ethanol]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub>(g) + H<sub>2</sub>O(g) ⇌ C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>5</sub>OH(l) | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Propene]] + [[Steam]] ⇌ [[Propanol]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>6</sub>(g) + H<sub>2</sub>O(g) ⇌ C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>7</sub>OH(l) | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Butene]] + [[Steam]] ⇌ [[Butanol]] | ||
| + | : C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub>(g) + H<sub>2</sub>O(g) ⇌ C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>9</sub>OH(l) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09667 ''Alkenes, page 149, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d38 ''Alkenes, page 77-80, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Alkenes, pages 147, 148, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Alkenes, pages 154-155, 158-159, 168, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Alkenes, pages 177-8, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Alkenes, pages 189, 195, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Alkenes, pages 227, 230-237, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Alkenes; formation in cracking reaction, page 176, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Alkenes; reactions of, pages 178-80, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Alkenes, page 275, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Alkenes, page 88, 90, 98, 99, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Alkenes, pages 138, 140, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Alkenes, pages 161, 173, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Alkenes, pages 256, 262, 263, 285-287, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Alkenes; reactions, pages 174-175, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Alkenes, page 143, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Alkenes, pages 232-233, 240-241, 242-243, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Alkenes, pages 88, 90, 94, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR Gateway ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:25, 30 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Alkenes are hydrocarbon compounds with one double bond and the general formula; CnH2n
About Alkenes
- Alkenes are a homologous series of hydrocarbon compounds.
- The functional group of the Alkenes is the double bonds between the Carbon atoms.
- Alkenes are long chains of Carbon atoms covalently bonded together with double and single bonds and Hydrogen atoms taking the remaining bonds.
- Alkenes are referred to as unsaturated hydrocarbons because the double bond means it is not saturated (full) with Hydrogen atoms.
- Testing for alkenes can be done by adding them to Bromine Water. If the Bromine Water turns from orange to colourless, then an alkene is present. During this test the Bromine reacts with the alkene to form a Bromoalkane.
- Ethene + Bromine → Dibromoethane
\(C_2H_4 + Br_2 → C_2H_4Br_2\)
Examples
| Ethene | Propene | But-1-ene | But-2-ene | |
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n) | C2H4 | C3H6 | C4H8 | C4H8 |
| Structural Formula | CH2CH2 | CH2CHCH3 | CH2CHCH2CH3 | CH3CHCHCH3 |
| Structural Diagram | ||||
| Ball and Stick Model |
Reactions of Alkenes
Combustion
During combustion of alkenes the Carbon and Hydrogen atoms are oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
Complete Combustion
Complete combustion occurs when there is enough Oxygen to completely Oxidise all of the atoms in the alkene. In the complete combustion of alkenes the only products are Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Ethene + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- C2H4 + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 2H2O
- Propene + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- 2C3H6 + 9O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
- Butene + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- C4H8 + 6O2 → 4CO2 + 4H2O
Incomplete Combustion
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is not enough Oxygen to Oxidise all of the atoms in the alkene. During incomplete combustion of alkenes the products may include Carbon (soot) and Carbon Monoxide.
- Ethene + Oxygen → Carbon Monoxide + Water
- C2H4 + 2O2 → 2CO + 2H2O
- Ethene + Oxygen → Soot + Carbon Monoxide + Water
- 2C2H4 + 3O2 → 2C + 2CO + 4H2O
Reaction with Halogens
When halogens are added to alkenes the double bond in the alkenes breaks and the halogens bond in its place.
Reaction with Hydrogen
Alkenes can be saturated with extra Hydrogen using a catalyst.
Reaction with Steam
Alkenes can react with steam to produce alcohols using a catalyst.
References
AQA
- Alkenes, page 149, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Alkenes, page 77-80, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Alkenes, pages 147, 148, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Alkenes, pages 154-155, 158-159, 168, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Alkenes, pages 177-8, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Alkenes, pages 189, 195, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Alkenes, pages 227, 230-237, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Alkenes; formation in cracking reaction, page 176, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Alkenes; reactions of, pages 178-80, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Alkenes, page 275, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Alkenes, page 88, 90, 98, 99, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Alkenes, pages 138, 140, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Alkenes, pages 161, 173, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Alkenes, pages 256, 262, 263, 285-287, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Alkenes; reactions, pages 174-175, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel