Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning

The hazard symbol for ionising radiation.
Ionising Radiation is radiation which can cause atoms to lose electrons and become ions.
About Ionising Radiation
- Ionising radiation damages living organisms.
- Ionising radiation may kill cells by damaging the parts inside them, particularly the DNA.
- Ionising radiation can cause the appearance of burns to the skin. A high enough dose of Ionising Radiation can cause instant death.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Ionising Radiation is radiation emitted from the nucleus of an atom which can cause other atoms to lose electrons and become ions.
About Ionising Radiation
- The units of exposure to ionising radiation are the Sievert which is 1 Joule of energy from ionising radiation being absorbed by 1 kilogram of flesh.
In Nuclear Physics there are three types of ionising radiation:
- Alpha Radiation - The emission of an alpha particle from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
- Beta Radiation - The emission of a beta particle from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
- Gamma Radiation - The emission of a gamma-ray from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
- Neutron Radiation - The emission of a neutron from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
Ionising Atoms
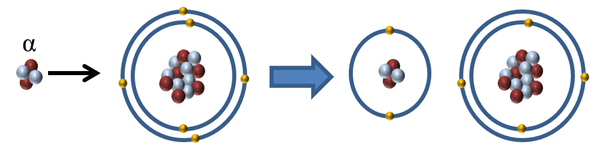
| When an alpha particle interacts with an atom the alpha particle can remove one or two electrons to ionise the atom. |
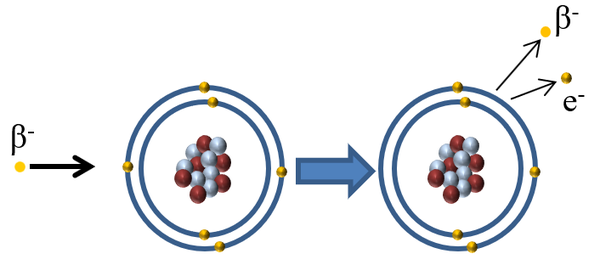
| When a Beta minus particle interacts with an atom the beta minus particle can pass on some of its kinetic energy to an electron in the outer shell causing the electron to escape ionising the atom. |
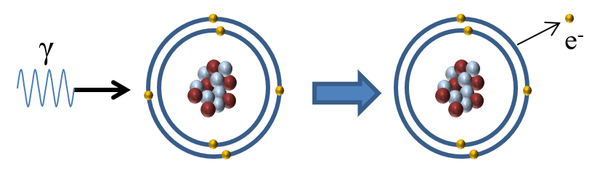
| When a gamma-ray interacts with an atom the gammarray is absorbed by an electron in the outer shell causing the electron to escape ionising the atom. |
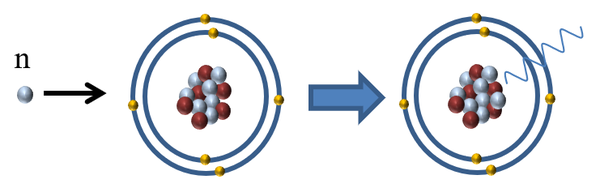
| Neutron radiation is referred to as indirectly ionising because it does not affect the electrons orbiting an atom but it can cause the release of directly ionising radiation in two ways: |
| It can be absorbed by a nucleus making it unstable and causing it to release a gamma-ray. |
| It can decay into a proton and a beta particle releasing a gamma-ray |
Comparison of Ionising Radiation
| Radiation | Symbol | Relative Penetration Depth | Relative Ionising Potential | Extra Info |
| Alpha Radiation | α | Low | High | Alpha is the least dangerous outside the body as it cannot penetrate the skin, but the most dangerous inside the body because it is the most highly ionising. |
| Beta Radiation | β- | Medium | Medium | Beta is equally dangerous inside as outside the body as easily penetrates skin. |
| Gamma Radiation | γ | High | Low | Gamma easily penetrates the skin but mostly passes through the body without interacting with any atoms. However, at high intensities it is extremely dangerous. |
| Neutron Radiation | n | High | Indirect | Neutrons are the most dangerous to living tissue as it penetrates the skin easily and is likely to be captured by the nucleus of atoms inside the body making them radioactive. |