Difference between revisions of "Electrical Bulb"
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
: In a [[Filament Bulb|filament]] '''bulb''' [[Electrical Work|electrical work]] is done to [[heat]] the filament to a high enough [[temperature]] that it glows in [[Visible Light|visible light]], see [[Black Body Radiation|black body radiation]]. | : In a [[Filament Bulb|filament]] '''bulb''' [[Electrical Work|electrical work]] is done to [[heat]] the filament to a high enough [[temperature]] that it glows in [[Visible Light|visible light]], see [[Black Body Radiation|black body radiation]]. | ||
: The [[Electrical Current|electrical current]] has a [[heating]] effect on the filament which increases its [[temperature]]. This causes the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] to increase, so the '''bulb''' does not behave as an [[Ohmic Conductor|ohmic conductor]]. | : The [[Electrical Current|electrical current]] has a [[heating]] effect on the filament which increases its [[temperature]]. This causes the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] to increase, so the '''bulb''' does not behave as an [[Ohmic Conductor|ohmic conductor]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===IV Graph=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:IVGraphBulb.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ====Description==== | ||
| + | The [[IV Graph]] for a '''bulb''' shows that: | ||
| + | *As [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] increases, [[Electrical Current|increases]]. | ||
| + | *At small [[Potential Difference|potential differences]]] the the relationship between [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] and [[Electrical Current|current]] is [[linear]] (the [[gradient]] is constant). | ||
| + | *At large [[Potential Difference|potential differences]] the [[gradient]] becomes more shallow as the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of the '''bulb''' increases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Explanation==== | ||
| + | : At small [[Potential Difference|potential differences]] there is a small [[Electrical Current|current]] so the [[heating]] effect of the [[Electrical Current|current]] is small and the [[filament]] remains at a low [[temperature]]. | ||
| + | : At large [[Potential Difference|potential differences]] there is a large [[Electrical Current|electrical current]] so the [[heating]] effect of the [[Electrical Current|current]] is large which causes the [[filament]] to be a high [[temperature]]. | ||
| + | :: This is caused by [[electron]]s in the [[wire]] [[collide|colliding]] with [[ion]]s in the [[metal]] [[lattice]] causing them to [[vibrate]]. | ||
| + | : [[Wire]]s (like the [[filament]]) have a greater [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] at higher [[temperature]]s, causing the increase in [[Electrical Current|current]] to be reduced. | ||
| + | :: This is because the more the [[ion]]s in the [[metal]] [[lattice]] [[vibrate]] the more likely [[electron]]s are to [[collide]] with them and slow down. | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 28 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 1
Meaning

This bulb has a filament inside it that glows when electricity goes through it.
A light bulb is something that lights up when you switch it on.
Key Stage 2
Meaning
An electrical bulb is a circuit component that gives out light when electricity goes through it.
About Electrical Bulbs
- There are many different kinds of electrical bulb.
- The type of electrical bulb you will use in class is called a Filament Bulb. It has a thin piece of wire inside that glows when electricity passes through it.
- Electrical bulbs can get very hot so you shouldn't touch the glass.
| An electrical bulb. | The symbol for an electrical bulb. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An electrical bulb is a circuit component that gives out light when electricity goes through it.
About Electrical Bulbs
- There are many different kinds of electrical bulb.
- The type of electrical bulb used in class is called a Filament Bulb. It has a thin piece of wire called a filament that becomes so hot when electricity passes through it that it begins to glow.
- Electrical bulbs can get very hot so you shouldn't touch the glass.
| An electrical bulb. | The symbol for an electrical bulb. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An electrical bulb is a circuit component that gives out light when electricity goes through it.
About Electrical Bulbs
- An electrical bulb usually refers to a Filament Bulb. However, there are other types.
- In a filament bulb electrical work is done to heat the filament to a high enough temperature that it glows in visible light, see black body radiation.
- The electrical current has a heating effect on the filament which increases its temperature. This causes the resistance to increase, so the bulb does not behave as an ohmic conductor.
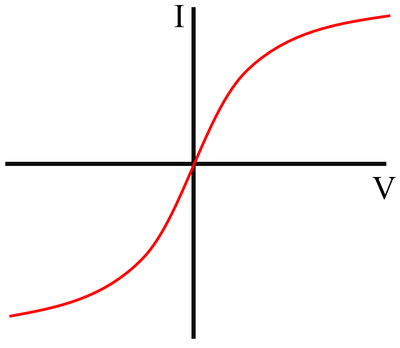
IV Graph
Description
The IV Graph for a bulb shows that:
- As potential difference increases, increases.
- At small potential differences] the the relationship between potential difference and current is linear (the gradient is constant).
- At large potential differences the gradient becomes more shallow as the resistance of the bulb increases.
Explanation
- At small potential differences there is a small current so the heating effect of the current is small and the filament remains at a low temperature.
- At large potential differences there is a large electrical current so the heating effect of the current is large which causes the filament to be a high temperature.
- Wires (like the filament) have a greater resistance at higher temperatures, causing the increase in current to be reduced.