Difference between revisions of "Hydrogen"
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Hydrogen]] is a [[gas]] that can catch fire easily. | [[Hydrogen]] is a [[gas]] that can catch fire easily. | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
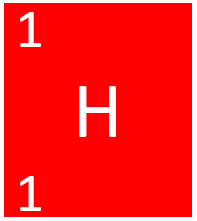
| + | [[File:HydrogenSymbol1.png|right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Hydrogen]].]] | ||
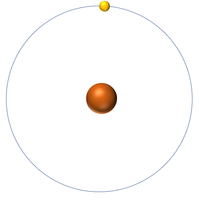
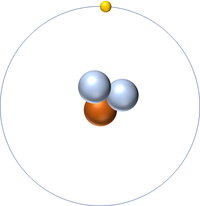
| + | [[File:H-1_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of a [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]] with 1 [[proton]] in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 1 [[electron]] orbiting the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | |||
[[Hydrogen]] is a [[non-metal]] [[element]] with 1 [[proton]] in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | [[Hydrogen]] is a [[non-metal]] [[element]] with 1 [[proton]] in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | [[File:HKS4.png|right|200px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Hydrogen]].]] | ||
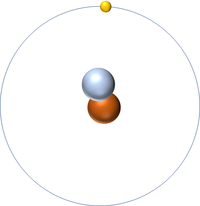
| + | [[File:H-1_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of the [[Bohr Model]] of a [[Hydrogen]]-1 [[isotope]] with 1 [[proton]] in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 1 [[electron]] in its [[Outer Shell|outer shell]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Hydrogen]] is a [[non-metal]] [[element]] with 1 [[proton]] in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | [[Hydrogen]] is a [[non-metal]] [[element]] with 1 [[proton]] in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 72: | ||
#Place a lit [[Wooden Splint|splint]] over the mouth of the [[Test Tube|test tube]]. | #Place a lit [[Wooden Splint|splint]] over the mouth of the [[Test Tube|test tube]]. | ||
#If a 'squeaky pop' [[sound]] is made then the [[gas]] is [[Hydrogen]]. | #If a 'squeaky pop' [[sound]] is made then the [[gas]] is [[Hydrogen]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Hydrogen, identification of, page 207, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Hydrogen, page 106, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Hydrogen, pages 109, 130-1, 280-1, 283-4, 286-7, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Hydrogen, pages 28, 8 6, 88-89, 122-123, 159, 184, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Hydrogen, pages 57, 134, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Hydrogen, pages 57, 159, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Hydrogen, test for, pages 160, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Hydrogen; bomb, page 131, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Hydrogen; test for, page 203, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Hydrogen; test for, page 257, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Hydrogen (as a fuel), page 139, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Hydrogen (as a fuel), pages 71, 89, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Hydrogen; as a fuel, pages 206, 207, 260, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Hydrogen; test for, page 126, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Hydrogen, pages 178-179, 186-187, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:50, 19 February 2021
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Hydrogen is a gas that can catch fire easily.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
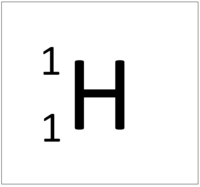
Hydrogen is a non-metal element with 1 proton in the nucleus.
About Hydrogen
Molecular Structure
Atomic Structure
- Hydrogen has 1 proton and 0 neutrons so it has an atomic mass of 1.
- An atom of hydrogen has one electron.
- A Hydrogen ion has usually lost its only electron to become positively charged.
Properties
- Hydrogen is a gas at room temperature.
- Hydrogen gas is less dense than air.
- Hydrogen reacts with Oxygen to form water.
Testing for Hydrogen
- Collect the gas in a test tube.
- Place a lit splint over the mouth of the test tube.
- If a 'squeaky pop' sound is made then the gas is Hydrogen.
Key Stage 4
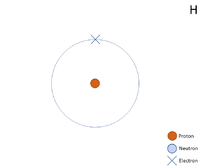
A 2 dimensional representation of the Bohr Model of a Hydrogen-1 isotope with 1 proton in the nucleus and 1 electron in its outer shell.
Meaning
Hydrogen is a non-metal element with 1 proton in the nucleus.
About Hydrogen
Molecular Structure
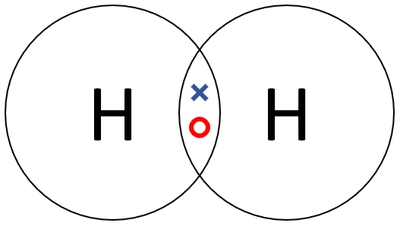
- Hydrogen has the chemical formula H2.
- Two Hydrogen atoms join together in a covalent bond.
| A dot and cross diagram of a Hydrogen molecule. |
Atomic Structure
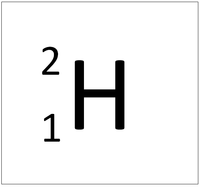
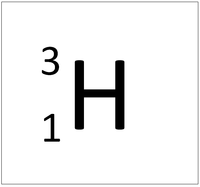
- The most common isotope of Hydrogen has 1 proton and 0 neutrons so it has an atomic mass of 1.
| Hydrogen | Deuterium | Tritium |
| Hydrogen always has 1 proton but isotope there are no neutrons. | Hydrogen always has 1 proton but in this isotope there is 1 neutron. This isotope of Hydrogen is known as Deuterium. | Hydrogen always has 1 proton but in this isotope there is 2 neutrons. This isotope of Hydrogen is known as Tritium. |
- An atom of hydrogen has one electron.
- A Hydrogen ion has usually lost its only electron to become positively charged.
Properties
- Hydrogen is a gas at standard temperature and pressure.
- Hydrogen gas is less dense than air.
- Hydrogen reacts with Oxygen to form water.
Testing for Hydrogen
- Collect the gas in a test tube.
- Place a lit splint over the mouth of the test tube.
- If a 'squeaky pop' sound is made then the gas is Hydrogen.
References
AQA
- Hydrogen, identification of, page 207, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Hydrogen, page 106, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Hydrogen, pages 109, 130-1, 280-1, 283-4, 286-7, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Hydrogen, pages 28, 8 6, 88-89, 122-123, 159, 184, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Hydrogen, pages 57, 134, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Hydrogen, pages 57, 159, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Hydrogen, test for, pages 160, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Hydrogen; bomb, page 131, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Hydrogen; test for, page 203, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Hydrogen; test for, page 257, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Hydrogen (as a fuel), page 139, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Hydrogen (as a fuel), pages 71, 89, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Hydrogen; as a fuel, pages 206, 207, 260, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Hydrogen; test for, page 126, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel