Difference between revisions of "Carbon"
(→Atomic Structure) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|} | |} | ||
====Atomic Structure==== | ====Atomic Structure==== | ||
| − | : The most common [[isotope]] of [[ | + | : The most common [[isotope]] of [[Carbon]] is [[Carbon-12]] which has 6 [[proton]]s and 6 [[neutron]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. |
: [[Carbon]] is in [[Period]] 2 of the [[Periodic Table]] because it has 2 [[Electron Orbital|electron shells]]. | : [[Carbon]] is in [[Period]] 2 of the [[Periodic Table]] because it has 2 [[Electron Orbital|electron shells]]. | ||
: [[Carbon]] has 4 [[electron]]s in its [[Outer Shell|outer shell]] so it can form 4 [[bond]]s with other [[atom]]s. | : [[Carbon]] has 4 [[electron]]s in its [[Outer Shell|outer shell]] so it can form 4 [[bond]]s with other [[atom]]s. | ||
| + | |||
====Properties==== | ====Properties==== | ||
: [[Carbon]] is [[solid]] at [[STP|room temperature]]. | : [[Carbon]] is [[solid]] at [[STP|room temperature]]. | ||
: The different [[allotropes]] have different [[Melting Point|melting points]] and different [[Electrical Conductivity|electrical conductivity]]. | : The different [[allotropes]] have different [[Melting Point|melting points]] and different [[Electrical Conductivity|electrical conductivity]]. | ||
Revision as of 20:53, 1 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Carbon is a chemical that makes diamonds and graphite.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Carbon is a non-metal element with an atomic number of 6.
About Carbon
Molecular Structure
- Carbon has the chemical symbol C.
Atomic Structure
- Carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic number of 6 and a atomic mass of 12.
- Carbon is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
Properties
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Carbon is a non-metal element, on the Periodic Table with 6 protons in the nucleus.
About Carbon
Molecular Structure
- Carbon has the chemical symbol C.
- Carbon forms covalent bonds with other Carbon atoms to produce a giant covalent structure.
- Carbon is able to make long chains of atoms to produce compounds called polymers.
There are several allotropes of Carbon including:
Examples
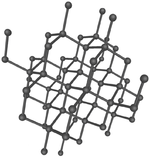
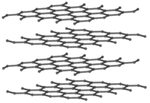
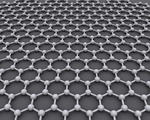
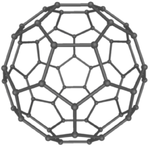
| Diamond is a giant covalent structure where each Carbon atom has 4 bonds with adjacent atoms. | Graphite has a giant covalent structure with each Carbon atom has 3 bonds with adjacent atoms in a layer with loose bonds between the layers. | Graphene has a giant covalent structure where each Carbon atom has 3 bonds with adjacent atoms forming a layer that is one atom thick. | Fullerenes have a giant covalent structure where each Carbon atom has 3 bonds with adjacent atoms forming a sphere. |
Atomic Structure
- The most common isotope of Carbon is Carbon-12 which has 6 protons and 6 neutrons in the nucleus.
- Carbon is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
- Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer shell so it can form 4 bonds with other atoms.
Properties
- Carbon is solid at room temperature.
- The different allotropes have different melting points and different electrical conductivity.