Difference between revisions of "Oxygen"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
[[File:OxygenSymbol1.png|right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Oxygen]].]] | [[File:OxygenSymbol1.png|right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Oxygen]].]] | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:O-16_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of a [[Oxygen]] [[atom]] with 8 [[proton]]s and 8 [[neutron]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 8 [[electron]]s orbiting the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]].]] |
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Oxygen]] is a [[Group 6]] [[non-metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 8. | [[Oxygen]] is a [[Group 6]] [[non-metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 8. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
[[File:OKS4.PNG|right|200px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Oxygen]].]] | [[File:OKS4.PNG|right|200px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Oxygen]].]] | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:O-16_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of the [[Bohr Model]] of a [[Oxygen]]-16 [[isotope]] with 8 [[proton]]s and 8 [[neutron]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 2 [[electron]]s in the first [[Electron Orbital|shell]] and 6 in the [[Outer Shell|outer shell]].]] |
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Oxygen]] is a [[Group 6]] [[non-metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 8 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | [[Oxygen]] is a [[Group 6]] [[non-metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 8 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:53, 19 February 2021
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Oxygen is a Group 6 non-metal element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 8.
About Oxygen
- Oxygen makes up 21% of the air.
- Oxygen has the chemical symbol O.
Molecular Structure
- The chemical formula for a Oxygen molecule is O2.
Atomic Structure
- Oxygen has 8 protons and 8 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic number of 8 and a atomic mass of 16.
- Oxygen is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
Properties
- Oxygen is a gas at room temperature.
Key Stage 4
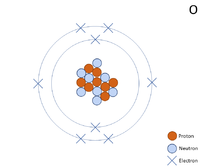
A 2 dimensional representation of the Bohr Model of a Oxygen-16 isotope with 8 protons and 8 neutrons in the nucleus and 2 electrons in the first shell and 6 in the outer shell.
Meaning
Oxygen is a Group 6 non-metal element, on the Periodic Table, with 8 protons in the nucleus.
About Oxygen
- Oxygen makes up 21% of the air.
- Oxygen has the chemical symbol O.
Molecular Structure
- The chemical formula for an Oxygen molecule is O2.
- Oxygen forms a covalent bond with another Oxygen atom to produce a simple covalent molecule.
Atomic Structure
- The most common stable isotope of Oxygen has 8 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 16.
- Oxygen is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
- Oxygen has 6 electrons in its outer shell and needs 2 more to get a full outer shell so it can form 2 bonds with other atoms.
Properties
Testing for Oxygen
- Collect the gas in a test tube.
- Place a glowing splint over the mouth of the test tube.
- If the splint relights then the gas is Oxygen.
References
AQA
- Oxygen, page 287, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Oxygen, pages 107, 184-5, 213, 292-5, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Oxygen, pages 184, 194-195, 197, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Oxygen, pages 52, 61, 124, 282, 288-289, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA

