Platinum
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
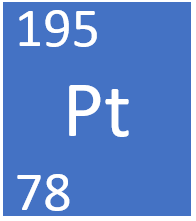
Platinum is a transition metal element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 78.
About Platinum
Molecular Structure
- Platinum has the chemical symbol Pt.
- Platinum atoms join together in large numbers to form a giant metal molecule.
Atomic Structure
- Platinum as 78 protons and 117 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 78 and an atomic mass of 195.
- Platinum is in Period 6 of the Periodic Table because it has 6 electron shells.
Properties
- Platinum is a metal element so it is a good thermal conductor and a good electrical conductor.
- Platinum is a shiny solid at room temperature.
- Platinum is malleable.
- Platinum is sonorous.
- Platinum is ductile.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Platinum is a transition metal element, on the Periodic Table, with 78 protons in the nucleus.
About Platinum
Molecular Structure
- Platinum has the chemical formula Pt.
- Platinum atoms join together in a giant metallic structure.
Atomic Structure
- The most stable isotope of Platinum has 117 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 195.
- Platinum is in Period 6 of the Periodic Table because it has 6 electron shells.
- Platinum loses electrons to form positive metal ions.
Properties
- Platinum forms ionic bonds with non-metals.
- Platinum is a metal element so it is a good thermal conductor and a good electrical conductor.
- Platinum is a shiny solid at standard temperature and pressure and has a high melting point.
- Platinum is malleable.
- Platinum is sonorous.
- Platinum is ductile.