Difference between revisions of "Electrolysis"
(→Key Stage 4) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
: [[Electrolysis]] cannot happen in [[solid]]s because the [[ion]]s [[vibrate]] around fixed positions in a [[solid]] and are not free to move. | : [[Electrolysis]] cannot happen in [[solid]]s because the [[ion]]s [[vibrate]] around fixed positions in a [[solid]] and are not free to move. | ||
: The [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] are [[attracted]] to the [[Negative Charge|negative]] [[electrode]] ([[cathode]]) and the [[Negative Ion|negative ions]] are [[attracted]] to the [[Positive Charge|positive]] [[electrode]] ([[anode]]). | : The [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] are [[attracted]] to the [[Negative Charge|negative]] [[electrode]] ([[cathode]]) and the [[Negative Ion|negative ions]] are [[attracted]] to the [[Positive Charge|positive]] [[electrode]] ([[anode]]). | ||
| − | : When the [[Negative Ion|negative ions]] reach the [[anode]] they lose [[electron]]s to become [[atom]]s or [[Neutral | + | : When the [[Negative Ion|negative ions]] reach the [[anode]] they lose [[electron]]s to become [[atom]]s or [[Neutral Charge|neutral]] [[compound]]s. |
: When the [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] reach the [[cathode]] they gain [[electron]]s to become [[atom]]s. However, in [[aqueous]] [[solution]] if the [[metal]] [[ion]]s are more [[reactivity|reactive]] than [[Hydrogen]] then [[Hydrogen]] [[gas]] will be [[product|produced]]. | : When the [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] reach the [[cathode]] they gain [[electron]]s to become [[atom]]s. However, in [[aqueous]] [[solution]] if the [[metal]] [[ion]]s are more [[reactivity|reactive]] than [[Hydrogen]] then [[Hydrogen]] [[gas]] will be [[product|produced]]. | ||
: To describe an [[electrolysis]] [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] [[Half Equation|half equations]] are used. | : To describe an [[electrolysis]] [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] [[Half Equation|half equations]] are used. | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 6 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Electrolysis is a process where compounds are decomposed by an electrical current.
About Electrolysis
- Electrolysis can be used to extract metals from minerals when the metal is more reactive than Carbon.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Electrolysis is a process in which an ionic compound is decomposed by passing an electrical current through it.
About Electrolysis
- In electrolysis two electrodes (an anode and a cathode) are placed in either a molten or aqueous ionic compound.
- Electrolysis cannot happen in solids because the ions vibrate around fixed positions in a solid and are not free to move.
- The positive ions are attracted to the negative electrode (cathode) and the negative ions are attracted to the positive electrode (anode).
- When the negative ions reach the anode they lose electrons to become atoms or neutral compounds.
- When the positive ions reach the cathode they gain electrons to become atoms. However, in aqueous solution if the metal ions are more reactive than Hydrogen then Hydrogen gas will be produced.
- To describe an electrolysis reaction half equations are used.
Examples
| Balanced Symbol Equation | 2Li2O(l) → 4Li(l) + O2(g) | CuCl2(aq) → Cu(s) + Cl2(g) | 2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g) |
| Half Equation at cathode | Li+ + e- → Li | Cu+2(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) | 2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g) |
| Half Equation at anode | 2O-2 → O2 + 4e- | 2Cl-(aq) → Cl2(g) + 2e- | 4OH- → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e- |
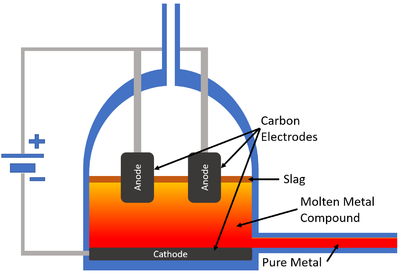
Electrolysis of Molten Ionic Compounds
- The electrolysis of molten ionic compounds decomposes those ionic compounds in a liquid state.
- The ionic compound must be heated and melted before electrolysis.
- Non-metal ionic elements or compounds will be collected at the anode where they lose their extra electrons.
- Metal ions will be collected at the cathode where they gain electrons.
| A diagram showing the electrolysis of a molten ionic compound in an electrolysis cell. |
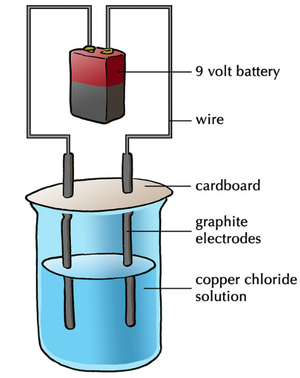
Electrolysis of Aqueous Ionic Compounds
- The electrolysis of aqueous ionic compounds decomposes those ionic compounds in solution.
- The electrolysis of aqueous ionic compounds will produce Hydrogen gas if the the metal elements is more reactive than Hydrogen.
- Non-metal ionic elements or compounds will be collected at the anode where they lose their extra electrons.
- Metal ions less reactive than Hydrogen will be collected at the cathode where they gain electrons.
- Metal ions more reactive than Hydrogen will displace Hydrogen atoms in the water after gaining [[electrons at the cathode. This causes Hydrogen gas to collect at the cathode.