Ionic Compound
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An ionic compound is a molecule formed from 2 or more elements which have transferred electrons to become ions.
About Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds form when atoms lose one or more electrons to become a positive ions and other atoms gain electrons to become negative ions. The electrostatic force of attraction between these ions is a strong chemical bond.
- Metal elements form positive ions because it is easier for them lose electrons than gain electrons to get a full outer shell. Metals are on the left hand side of the Periodic Table and usually have either 1, 2, 3 or 4 electrons in the Outer Shell.
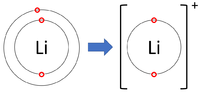
- Group 1 Elements all form +1 ions; Li+1, Na+1, K+1
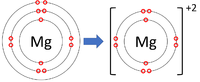
- Group 2 Elements all form +2 ions; Be+2, Mg+2, Ca+2
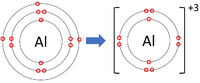
- Group 3 Elements all form +3 ions; Al+3
- Transition Metal Elements can form different ions which are shown by Roman Numerals; Iron can form Fe(II) which is Fe+2 or Fe(III) is Fe+3,
Manganese can form Mn (II) which is Mn+2 or Mn (IV) which is Mn +4
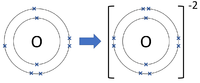
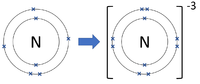
- Non-metal elements form negative ions because it is easier for them to gain electrons than lose electrons to get a full outer shell. Non-metals are on the right hand side of the Periodic Table and usually have 4, 5, 6, 7 or 8 electrons in their outer shell.
- Group 5 Elements all form -3 ions; N-3, P-3
- Group 6 Elements all form -2 ions; O-2, S-2
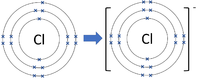
- Group 7 Elements all form -1 ions; F-1, Cl-1
- Some covalent compounds can form negative ions; Carbonate forms -2 ions CO3-2, Sulphate forms -2 ions SO4-2, Nitrate forms -1 ions NO3-1
Examples
| Lithium forms +1 ions. | Magnesium forms +2 ions. | Aluminium forms +3 ions. |
| Chlorine forms -1 ions. | Oxygen forms -2 ions. | Nitrogen forms -3 ions. |
Bulk Properties
- In their solid state ionic compounds are poor electrical conductors because the ions are not free to move.
- In their liquid state ionic compounds are good electrical conductors because the electrically charged ions are free to move.
- Most ionic compounds are soluble in water.
- When dissolved in solution ionic compounds are good electrical conductors because the electrically charged ions are free to move.
- Ionic compounds form giant ionic structures which have high melting points due to the strong electrostatic force between the ions.
| State | Electrical Conductivity | Reason |
| Solid | Poor | Ions are in fixed positions and not free to move. |
| Liquid (Molten) | Good | Ions are free to move in the liquid. |
| Dissolved in Solution (Aqueous) | Good | Ions are free to move through solution. |
References
Edexcel
- Ionic compounds, page 180, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Ionic compounds, page 36, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Ionic compounds, pages 20-22, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Ionic compounds, pages 49-55, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Ionic compounds, pages 83-85, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Ionic compounds; properties, pages 38-39, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel