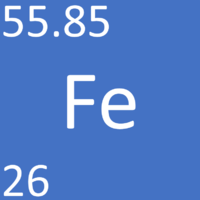Difference between revisions of "Iron"
(→Properties) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 2== | ==Key Stage 2== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Iron]] is a [[metal]]. | + | [[Iron]] is a [[magnetic]] [[metal]]. |
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:IronSymbol1.png|right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Iron]].]] |
[[Iron]] is a [[Transition Metal|transition metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 26. | [[Iron]] is a [[Transition Metal|transition metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 26. | ||
===About Iron=== | ===About Iron=== | ||
====Molecular Structure==== | ====Molecular Structure==== | ||
| − | : [[Iron]] has the [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] [[Iron| | + | : [[Iron]] has the [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] [[Iron|Fe]]. |
: [[Iron]] [[atom]]s join together in large numbers to form a giant [[metal]] [[molecule]]. | : [[Iron]] [[atom]]s join together in large numbers to form a giant [[metal]] [[molecule]]. | ||
| + | |||
====Atomic Structure==== | ====Atomic Structure==== | ||
: [[Iron]] as 26 [[proton]]s and 30 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Atomic Number]] of 26 and an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 56. | : [[Iron]] as 26 [[proton]]s and 30 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Atomic Number]] of 26 and an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 56. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | [[File:FeKS4.PNG|right|200px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Iron]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Iron]] is a [[Transition Metal|transition metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 26 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | [[Iron]] is a [[Transition Metal|transition metal]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 26 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | ||
| − | ===About | + | ===About Iron=== |
====Molecular Structure==== | ====Molecular Structure==== | ||
| − | : [[Iron]] has the [[Chemical Formula|chemical formula]] [[Iron | | + | : [[Iron]] has the [[Chemical Formula|chemical formula]] [[Iron |Fe]]. |
: [[Iron]] [[atom]]s join together in a [[Giant Metallic Structure|giant metallic structure]]. | : [[Iron]] [[atom]]s join together in a [[Giant Metallic Structure|giant metallic structure]]. | ||
| + | |||
====Atomic Structure==== | ====Atomic Structure==== | ||
: The most [[Stable Isotope|stable isotope]] of [[Iron]] has 30 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 56. | : The most [[Stable Isotope|stable isotope]] of [[Iron]] has 30 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 56. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 44: | ||
: [[Iron]] is [[ductile]]. | : [[Iron]] is [[ductile]]. | ||
: [[Iron]] is [[magnetic]]. | : [[Iron]] is [[magnetic]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Iron, page 138, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Iron, pages 163, 285, 287, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Iron, pages 216-217, 220-221, 223, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Iron, pages 242-3, 287, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Iron, pages 208-209, 216-219, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:13, 5 March 2020
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Iron is a transition metal element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 26.
About Iron
Molecular Structure
- Iron has the chemical symbol Fe.
- Iron atoms join together in large numbers to form a giant metal molecule.
Atomic Structure
- Iron as 26 protons and 30 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 26 and an atomic mass of 56.
- Iron is in Period 4 of the Periodic Table because it has 4 electron shells.
Properties
- Iron is a metal element so it is a good thermal conductor and a good electrical conductor.
- Iron is a shiny solid at room temperature.
- Iron is malleable.
- Iron is sonorous.
- Iron is ductile.
- Iron is magnetic.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Iron is a transition metal element, on the Periodic Table, with 26 protons in the nucleus.
About Iron
Molecular Structure
- Iron has the chemical formula Fe.
- Iron atoms join together in a giant metallic structure.
Atomic Structure
- The most stable isotope of Iron has 30 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 56.
- Iron is in Period 4 of the Periodic Table because it has 4 electron shells.
- Iron loses electrons to form positive metal ions.
Properties
- Iron forms ionic bonds with non-metals.
- Iron is a metal element so it is a good thermal conductor and a good electrical conductor.
- Iron is a shiny solid at standard temperature and pressure and has a high melting point.
- Iron is malleable.
- Iron is sonorous.
- Iron is ductile.
- Iron is magnetic.
References
AQA
- Iron, page 138, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Iron, pages 163, 285, 287, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Iron, pages 216-217, 220-221, 223, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Iron, pages 242-3, 287, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA