Difference between revisions of "Transition Metal"
(→Density) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===About Transition Metals=== | ===About Transition Metals=== | ||
| + | : [[Transition Metal]]s have the [[Physical Property|physical properties]] of [[metal]]s. | ||
| + | : [[Transition Metal]]s [[Chemical Bond|bond]] together with [[Metallic Bond|metallic bonds]] in which [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] are surrounded by a sea of [[Negative Charge|negatively charged]] [[electron]]s (known as [[Delocalised Electrons|delocalised electrons]]. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 59: | Line 61: | ||
====Melting Point==== | ====Melting Point==== | ||
| − | : [[Transition Metal]]s usually have high [[Melting Point|melting points]]. | + | : [[Transition Metal]]s usually have high [[Melting Point|melting points]] because [[Metallic Bond|metallic bonds]] are very strong, keeping the [[atom]]s [[Vibration|vibrating]] in fixed positions. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:center;" |The '''transition metal''' [[Melting Point|melting points]] measured in [[Kelvin]] are written below each [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]]. | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:center;" |The '''transition metal''' [[Melting Point|melting points]] measured in [[Kelvin]] are written below each [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]]. | ||
| Line 78: | Line 80: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====Reactivity==== |
| + | : The [[Transition Metal]]s are much less [[Reactivity|reactive]] than [[element]]s in [[Group 1|group 1]] and [[Group 2|group 2]]. | ||
| + | : Most of the [[Transition Metal]]s [[Chemical Reaction|react]] slowly with [[Oxygen]], [[Water]] and the [[Halogen]]s at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]] and some will not [[Chemical Reaction|react]] at all. | ||
| + | : For [[combustion]] to occur the [[Transition Metal]]s must be heated to very high [[temperature]]s. However, some [[Transition Metal]]s will not [[combustion|combust]] at all. | ||
| + | |||
====Ion Formation==== | ====Ion Formation==== | ||
| − | + | : [[Transition Metal]]s form [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] during [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reactions]]. | |
| + | |||
====Catalysts==== | ====Catalysts==== | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 18 December 2018
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Transition Metals (also known as transition elements) are a block of elements on the Periodic Table between Group 2 and Group 3.
About Transition Metals
- Transition Metals have the physical properties of metals.
- Transition Metals bond together with metallic bonds in which positive ions are surrounded by a sea of negatively charged electrons (known as delocalised electrons.
| Period 4 | 21Sc | 22Ti | 23V | 24Cr | 25Mn | 26Fe | 27Co | 28Ni | 29Cu | 30Zn |
| Period 5 | 39Y | 40Zr | 41Nb | 42Mo | 43Tc | 44Ru | 45Rh | 46Pd | 47Ag | 48Cd |
| Period 6 | 57La | 72Hf | 73Ta | 74W | 75Re | 76Os | 77Ir | 78Pt | 79Au | 80Hg |
| Period 7 | 89Ac | 104Rf | 105Db | 106Sg | 107Bh | 108Hs | 109Mt | 110Ds | 111Rg | 112Cn |
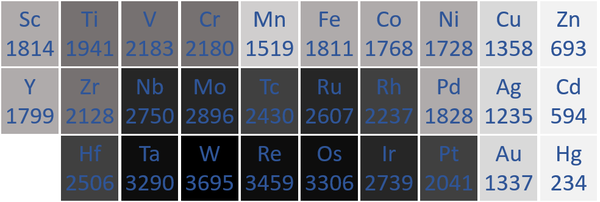
Melting Point
- Transition Metals usually have high melting points because metallic bonds are very strong, keeping the atoms vibrating in fixed positions.
| The transition metal melting points measured in Kelvin are written below each chemical symbol. |
| N.B. The Period 7 elements have not been included as they do not occur naturally and have not been made in large enough quantities to find their melting points. |
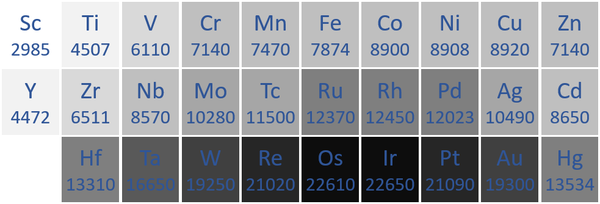
Density
- Transition Metals have a high density compared to other elements. However, many of the Actinides also have a density.
| The transition metal densities measured in kilograms per metre cubed are written below each chemical symbol. |
| N.B. The Period 7 elements have not been included as they do not occur naturally and have not been made in large enough quantities to find their [density|densities]]. |
Reactivity
- The Transition Metals are much less reactive than elements in group 1 and group 2.
- Most of the Transition Metals react slowly with Oxygen, Water and the Halogens at room temperature and some will not react at all.
- For combustion to occur the Transition Metals must be heated to very high temperatures. However, some Transition Metals will not combust at all.
Ion Formation
- Transition Metals form positive ions during chemical reactions.