Neutron Radiation
Revision as of 19:57, 7 March 2019 by NRJC (talk | contribs) (Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== neutron radiation is a type of non-ionising radiation emitted from the Atomic Nucleus|nucl...")
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
neutron radiation is a type of non-ionising radiation emitted from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
About Neutron Radiation
- Neutron radiation is a neutron emitted from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
- Neutrons have a relative atomic mass of 1 and relative charge of 0.
- Neutrons are emitted when the ratio of neutrons to protons is too large or when a massive unstable nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei in a process of nuclear fission.
Charge
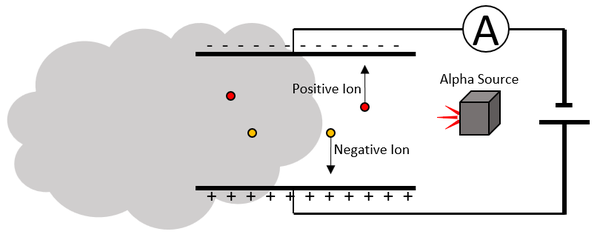
| Scientist were able to determine the charge of a neutron by sending it between two electrically charged plates and observing its path.
The neutron continues in a straight line so it must be neutral. |
Penetration Depth
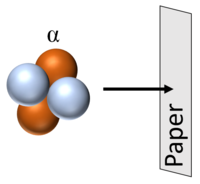
| Alpha particles can travel around 5cm through air (STP) before colliding with and ionising atoms or molecules. |
| Alpha particles can be stopped by a thin sheet of paper. |
Ionising Potential
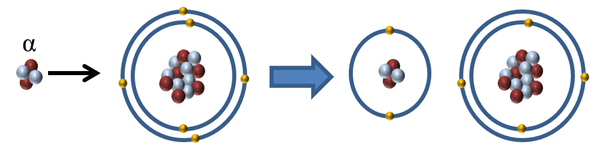
- With a charge of +2, α-particles are the most ionising of the three ionising radiations. It is capable of removing two electrons from a single atom or molecule or removing 1 electron from two atoms or molecules.
| When an α-particle interacts with an atom the α-particle can remove one or two electrons to ionise the atom. |
Precautions
- Alpha radiation is the most ionising but the least penetrating.
- Alpha sources are kept inside a block of lead with a hole that only allows the alpha particles out in one direction.
- Outside the body an organism can be protected from alpha radiation by keeping a distance greater than 5cm or by covering any bare skin.
- Inside an organism alpha particles are the most dangerous as they are highly ionising and there is nothing inside an organism to block them ionising biological molecules like DNA. Every precaution must be taken not to contaminate the skin with the alpha source in case it finds its way into the body through a cut or the mouth.
- When handling a source of beta radiation the precautions which should be taken are:
- Wear gloves - to prevent contamination.
- Use tongs to handle the source, never touch it - to prevent contamination.
- Aim the source away from any living organism - to prevent irradiation.
- Store the source in a sealed container - to prevent contamination and irradiation.
Applications
| In a smoke detector alpha particles are released between two electrodes.
When the alpha particles ionise the molecules in the air the ions move between the electrodes and a current flows in the circuit. When smoke gets between the electrodes the ions become stuck in large particles of soot preventing them from moving. This stops the current in the circuit. The ammeter in the circuit is connected to an alarm which goes off when there is no current. |