Difference between revisions of "Beryllium"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 2== ===Meaning=== Beryllium is a metal. ==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol...") |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Beryllium]] is a [[metal]]. | [[Beryllium]] is a [[metal]]. | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:BerylliumSymbol1.png|right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Beryllium]].]] | ||
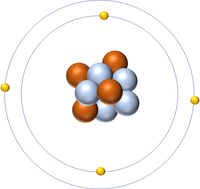
| + | [[File:Be-9_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of a [[Beryllium]] [[atom]] with 4 [[proton]]s and 5 [[neutron]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 4 [[electron]]s orbiting the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | + | [[Beryllium]] is a [[Group 2]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 4. | |
| − | [[Beryllium]] is a [[Group 2]] [[element]] , on the [[Periodic Table]], with an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 4. | ||
===About Beryllium=== | ===About Beryllium=== | ||
| − | : [[Beryllium]] has the [[Chemical | + | ====Molecular Structure==== |
| + | : [[Beryllium]] has the [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] [[Beryllium|Be]]. | ||
| + | : [[Beryllium]] [[atom]]s join together in large numbers to form a giant [[metal]] [[molecule]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Atomic Structure==== | ||
: [[Beryllium]] as 4 [[proton]]s and 5 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Atomic Number]] of 4 and an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 9. | : [[Beryllium]] as 4 [[proton]]s and 5 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Atomic Number]] of 4 and an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 9. | ||
| − | : [[Beryllium]] is the least [[Reactivity|reactive]] | + | : An [[atom]] of [[Beryllium]] has only 2 [[electron]]s in its [[Outer Shell|outer shell]]. |
| + | ====Properties==== | ||
| + | : [[Beryllium]] is the least [[Reactivity|reactive]] [[Alkali Earth Metal|alkali earth metal]]. | ||
: [[Beryllium]] is more [[Reactivity|reactive]] than [[Carbon]] on the [[Reactivity Series|reactivity series]] so it must be [[Extraction of Metals|extracted]] from its [[ore]] using [[electrolysis]]. | : [[Beryllium]] is more [[Reactivity|reactive]] than [[Carbon]] on the [[Reactivity Series|reactivity series]] so it must be [[Extraction of Metals|extracted]] from its [[ore]] using [[electrolysis]]. | ||
| − | : [[Beryllium]] [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] strongly with [[steam]] to produce [[Hydrogen]] [[gas]] and [[Beryllium Hydroxide]] | + | : [[Beryllium]] [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] strongly with [[steam]] to produce [[Hydrogen]] [[gas]] and [[Beryllium Hydroxide]] and [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] strongly with [[acid]]s to produce a [[Beryllium]] [[salt]]. |
| − | + | : [[Lithium]] is a [[solid]] at [[STP|room temperature]]. | |
| − | : [[ | + | |
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | [[File:BeKS4.PNG|right|200px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Beryllium]].]] | ||
| + | [[File:Be-9_WK.PNG|right|200px|thumb|A 2 dimensional representation of the [[Bohr Model]] of a [[Beryllium]]-9 [[isotope]] with 4 [[proton]]s and 5 [[neutron]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] and 2 [[electron]]s in the first [[Electron Orbital|shell]] and 2 in the [[Outer Shell|outer shell]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Beryllium]] is a [[Group 2]] [[element]] , on the [[Periodic Table]], with 4 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | + | [[Beryllium]] is a [[Group 2]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 4 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. |
===About Beryllium=== | ===About Beryllium=== | ||
| − | : [[Beryllium]] has the [[Chemical | + | ====Molecular Structure==== |
| + | : [[Beryllium]] has the [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] [[Beryllium|Be]]. | ||
| + | : [[Beryllium]] [[atom]]s join together in a [[Giant Metallic Structure|giant metallic structure]]. | ||
| + | ====Atomic Structure==== | ||
: The most [[Stable Isotope|stable isotope]] of [[Beryllium]] has 5 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 9. | : The most [[Stable Isotope|stable isotope]] of [[Beryllium]] has 5 [[neutron]]s in its [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] giving it an [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] of 9. | ||
| − | : [[Beryllium]] is the least [[Reactivity|reactive]] | + | : An [[atom]] of [[Beryllium]] has only 2 [[electron]]s in its [[Outer Shell|outer shell]]. |
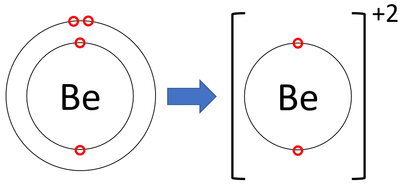
| + | : [[Beryllium]] [[ion]]s have lost two [[electron]]s to become [[Positive Charge|positively charged]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:BerylliumIonFormation.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the formation of a [[Beryllium]] [[ion]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Properties==== | ||
| + | : [[Beryllium]] is the least [[Reactivity|reactive]] [[Alkali Earth Metal|alkali earth metal]]. | ||
: [[Beryllium]] is more [[Reactivity|reactive]] than [[Carbon]] on the [[Reactivity Series|reactivity series]] so it must be [[Extraction of Metals|extracted]] from its [[ore]] using [[electrolysis]]. | : [[Beryllium]] is more [[Reactivity|reactive]] than [[Carbon]] on the [[Reactivity Series|reactivity series]] so it must be [[Extraction of Metals|extracted]] from its [[ore]] using [[electrolysis]]. | ||
| − | : [[Beryllium]] [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] strongly with [[steam]] to produce [[Hydrogen]] [[gas]] and [[Beryllium Hydroxide]]. | + | : [[Beryllium]] [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] strongly with [[steam]] to produce [[Hydrogen]] [[gas]] and [[Beryllium Hydroxide]] and [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] strongly with [[acid]]s to produce a [[Beryllium]] [[salt]]. |
| − | : | + | : [[Beryllium]] is a [[solid]] at [[STP|standard temperature and pressure]]. |
| − | : [[Beryllium]] [[ | + | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |[[File:Beryllium.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:BerylliumSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
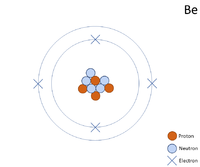
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" colspan = "2"|[[Beryllium]] always has 4 [[proton]]s. The most [[Stable Isotope|stable]] [[isotope]] has 5 [[neutron]]s. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:52, 19 February 2021
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Beryllium is a Group 2 element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 4.
About Beryllium
Molecular Structure
- Beryllium has the chemical symbol Be.
- Beryllium atoms join together in large numbers to form a giant metal molecule.
Atomic Structure
- Beryllium as 4 protons and 5 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 4 and an atomic mass of 9.
- An atom of Beryllium has only 2 electrons in its outer shell.
Properties
- Beryllium is the least reactive alkali earth metal.
- Beryllium is more reactive than Carbon on the reactivity series so it must be extracted from its ore using electrolysis.
- Beryllium reacts strongly with steam to produce Hydrogen gas and Beryllium Hydroxide and reacts strongly with acids to produce a Beryllium salt.
- Lithium is a solid at room temperature.
Key Stage 4
A 2 dimensional representation of the Bohr Model of a Beryllium-9 isotope with 4 protons and 5 neutrons in the nucleus and 2 electrons in the first shell and 2 in the outer shell.
Meaning
Beryllium is a Group 2 element, on the Periodic Table, with 4 protons in the nucleus.
About Beryllium
Molecular Structure
- Beryllium has the chemical symbol Be.
- Beryllium atoms join together in a giant metallic structure.
Atomic Structure
- The most stable isotope of Beryllium has 5 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 9.
- An atom of Beryllium has only 2 electrons in its outer shell.
- Beryllium ions have lost two electrons to become positively charged.
| A diagram showing the formation of a Beryllium ion. |
Properties
- Beryllium is the least reactive alkali earth metal.
- Beryllium is more reactive than Carbon on the reactivity series so it must be extracted from its ore using electrolysis.
- Beryllium reacts strongly with steam to produce Hydrogen gas and Beryllium Hydroxide and reacts strongly with acids to produce a Beryllium salt.
- Beryllium is a solid at standard temperature and pressure.
| Beryllium always has 4 protons. The most stable isotope has 5 neutrons. | |