Difference between revisions of "Gamma-ray"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | '''Gamma-rays''' are a type of [[Ionising Radiation|ionising radiation]] and the highest [[frequency]] and shortest [[wavelength]] of [[Electromagnetic Wave|electromagnetic wave]]. | + | '''Gamma-rays''' are a type of [[Ionising Radiation|ionising radiation]] [[emit]]ed from the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] of an [[Unstable Isotope|unstable isotope]] and are the highest [[frequency]] and shortest [[wavelength]] of [[Electromagnetic Wave|electromagnetic wave]]. |
| − | ===About Gamma-rays=== | + | ===About Gamma-rays as Electromagnetic Waves=== |
: [[Gamma-ray]]s are [[Transverse Wave|transverse waves]]. | : [[Gamma-ray]]s are [[Transverse Wave|transverse waves]]. | ||
: [[Gamma-ray]]s can travel through a [[vacuum]] as well as through [[gas]]es in the [[Earth's Atmosphere|Earth's atmosphere]]. | : [[Gamma-ray]]s can travel through a [[vacuum]] as well as through [[gas]]es in the [[Earth's Atmosphere|Earth's atmosphere]]. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
: [[Gamma-ray]]s can cause cancer because [[gamma-ray]]s can [[penetrate]] soft [[tissue]] and can ionise and damage [[DNA]] [[molecule]]s in the body [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] leading to a [[mutation]]. | : [[Gamma-ray]]s can cause cancer because [[gamma-ray]]s can [[penetrate]] soft [[tissue]] and can ionise and damage [[DNA]] [[molecule]]s in the body [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] leading to a [[mutation]]. | ||
: High intensity [[gamma-ray]]s can cause [[Radiation Sickness|radiation sickness]] because they can ionise and damage all parts of a [[Cell (Biology)|biology]] killing that [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | : High intensity [[gamma-ray]]s can cause [[Radiation Sickness|radiation sickness]] because they can ionise and damage all parts of a [[Cell (Biology)|biology]] killing that [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Gamma Rays as Ionising Radiation=== | ||
| + | : '''Gamma-rays''' may also be referred to as '''gamma radiation''' and is written with the symbol '''γ'''. | ||
| + | : '''Gamma-rays''' are a the highest [[frequency]] [[Electromagnetic Wave|electromagnetic wave]]. | ||
| + | : '''Gamma-rays''' have a [[Relative Atomic Mass|relative atomic mass]] of 0 and [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative charge]] of 0. | ||
| + | : '''Gamma-rays''' are [[emit]]ted when a [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is has excess [[Vibrational Energy|vibrational energy]] after it has [[Radioactive Decay|decayed]] via [[Alpha Particle|alpha]] or [[Beta Particle|beta]] [[emission]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Charge==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:GammaRayCharge.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:left;" |Scientist were able to determine the [[Electrical Charge|charge]] of a [[Gamma-ray|γ-ray]] by sending it between two [[Electrical Charge|electrically charged]] plates and observing its path. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''γ-ray''' continues in a straight line so it must be [[Neutral Charge|neutral]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Penetration Depth==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:GammaPenetrationAir.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:left;" |[[Gamma-ray|Gamma-rays]] can travel an infinite distance through [[air]] and the chances of [[colliding]] with an [[atom]] or [[molecule]] are almost non-existent. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:GammaPenetration.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:left;" |[[Gamma-ray|Gamma-rays]] can penetrate paper and sheets of [[metal]] foil but cannot penetrate more than a few 5cm of [[Lead]] or a [[metre]] of [[concrete]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Ionising Potential==== | ||
| + | : With no [[Electrical Charge|electrical charge]], '''γ-rays''' are the least [[Ionising Radiation|ionising]] of the three [[Ionising Radiation|ionising radiations]]. It is capable of knocking out one [[electron]] from an [[atom]] or [[molecule]] by being [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbed]] by an [[electron]] in the [[Outer Shell|outer shell]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:GammaIonise.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |When a [[Gamma-ray|gamma-ray]] interacts with an [[atom]] the [[Gamma-ray|gammarray]] is [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbed]] by an [[electron]] in the [[Outer Shell|outer shell]] causing the [[electron]] to escape '''ionising''' the [[atom]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Precautions=== | ||
| + | : [[Gamma-ray|Gamma radiation]] is the least [[Ionising Radiation|ionising]] but most [[Penetration Depth|penetrating]]. | ||
| + | : [[Gamma-ray]] sources are kept inside a block of [[lead]] with a hole that only allows the [[Gamma-ray|gamma-rays]] out in one direction. | ||
| + | : Outside the body an [[organism]] cannot easily be protected from [[Gamma-ray|gamma radiation]] as it can pass through the [[air]] unobstructed and needs thick sheets of [[Lead]] to block it. [[Gamma-ray|Gamma radiation]] can pass through the [[skin]] and [[Ionising Radiation|ionise]] [[tissue]] deep within the body. | ||
| + | : When handling a source of [[Gamma-ray|gamma radiation]] the precautions which should be taken are: | ||
| + | :*Wear gloves - to prevent [[Radioactive Contamination|contamination]]. | ||
| + | :*Use tongs to handle the source, never touch it - to prevent [[Radioactive Contamination|contamination]]. | ||
| + | :*Stand behind a thick sheet of [[Lead]] when not using it - to prevent [[irradiation]]. | ||
| + | :*Aim the source away from any living [[organism]] - to prevent [[irradiation]]. | ||
| + | :*Store the source in a sealed [[Lead]] container - to prevent [[Radioactive Contamination|contamination]] and [[irradiation]]. | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 7 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Gamma-rays are a type of ionising radiation emited from the nucleus of an unstable isotope and are the highest frequency and shortest wavelength of electromagnetic wave.
About Gamma-rays as Electromagnetic Waves
- Gamma-rays are transverse waves.
- Gamma-rays can travel through a vacuum as well as through gases in the Earth's atmosphere.
- The speed of gamma-rays through a vacuum is 300,000,000m/s.
As a wave gamma-rays can be:
- Transmitted - Gamma-rays can pass through a medium.
- Absorbed - The energy transferred by gamma-rays can be taken in by certain materials.
- Refracted - Gamma-rays can change direction when they cross the interface between two media.
However, unlike most waves gamma-rays cannot be:
- Reflected - There are no known materials on Earth that can reflect gamma-rays.
Unique Properties
- Gamma-rays are the highest energy electromagnetic waves.
- Gamma-rays are emitted from the atomic nucleus of unstable radioactive isotopes.
- Gamma-rays cause electrons in materials to gain enough energy to leave atoms creating ions which can destroy chemical bonds.
- Gamma-rays are the most penetrating, but least ionising form of Ionising Radiation.
- Gamma-rays can penetrate most materials except for thick lead and thick sheets of other elements more dense than lead on the periodic table.
- Gamma-rays cannot pass through heavy metals (metals with a high atomic mass).
Applications
- Gamma-rays can be used to sterilise food and medical equipment because it causes electrons in materials to gain enough energy to leave atoms creating ions which can destroy chemical bonds in micro-organisms thereby destroying the micro-organism.
- Gamma-rays can be used to irradiate cancerous tumors because they ionise atoms, destroying chemical bonds and can kill the cells. Cancer cells are weaker than healthy cells so more of the cancer cells will be killed than healthy ones.
- Gamma-rays cab be used to trace the flow of fluids through organs because Gamma-rays are emitted from the atomic nucleus of unstable radioactive isotopes which can be injected into a patient and they can penetrate most materials so they leave the body without being reflected, refracted or absorbed by the tissue.
Dangers
- Gamma-rays can cause cancer because gamma-rays can penetrate soft tissue and can ionise and damage DNA molecules in the body cells leading to a mutation.
- High intensity gamma-rays can cause radiation sickness because they can ionise and damage all parts of a biology killing that cell.
About Gamma Rays as Ionising Radiation
- Gamma-rays may also be referred to as gamma radiation and is written with the symbol γ.
- Gamma-rays are a the highest frequency electromagnetic wave.
- Gamma-rays have a relative atomic mass of 0 and relative charge of 0.
- Gamma-rays are emitted when a nucleus is has excess vibrational energy after it has decayed via alpha or beta emission.
Charge
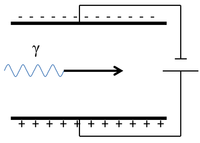
| Scientist were able to determine the charge of a γ-ray by sending it between two electrically charged plates and observing its path.
The γ-ray continues in a straight line so it must be neutral. |
Penetration Depth
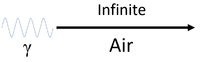
| Gamma-rays can travel an infinite distance through air and the chances of colliding with an atom or molecule are almost non-existent. |
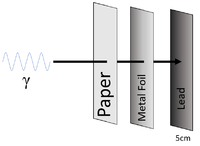
| Gamma-rays can penetrate paper and sheets of metal foil but cannot penetrate more than a few 5cm of Lead or a metre of concrete. |
Ionising Potential
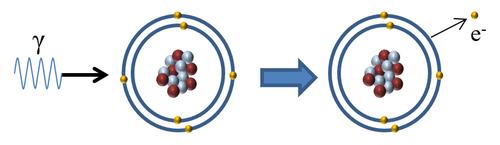
- With no electrical charge, γ-rays are the least ionising of the three ionising radiations. It is capable of knocking out one electron from an atom or molecule by being absorbed by an electron in the [[Outer Shell|outer shell].
| When a gamma-ray interacts with an atom the gammarray is absorbed by an electron in the outer shell causing the electron to escape ionising the atom. |
Precautions
- Gamma radiation is the least ionising but most penetrating.
- Gamma-ray sources are kept inside a block of lead with a hole that only allows the gamma-rays out in one direction.
- Outside the body an organism cannot easily be protected from gamma radiation as it can pass through the air unobstructed and needs thick sheets of Lead to block it. Gamma radiation can pass through the skin and ionise tissue deep within the body.
- When handling a source of gamma radiation the precautions which should be taken are:
- Wear gloves - to prevent contamination.
- Use tongs to handle the source, never touch it - to prevent contamination.
- Stand behind a thick sheet of Lead when not using it - to prevent irradiation.
- Aim the source away from any living organism - to prevent irradiation.
- Store the source in a sealed Lead container - to prevent contamination and irradiation.