Difference between revisions of "Group (Chemistry)"
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===About Groups=== | ===About Groups=== | ||
| + | : [[Helium]], in [[Group 0]] is an exception to this rule as it has 2 [[electron]]s in its [[Outer Shell]]. | ||
: The [[element]]s are arranged '''groups''' of similar [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]]. | : The [[element]]s are arranged '''groups''' of similar [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]]. | ||
: [[Element]]s have similar [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] when they have the same number of [[electron]]s in the [[Outer Shell]]. | : [[Element]]s have similar [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] when they have the same number of [[electron]]s in the [[Outer Shell]]. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
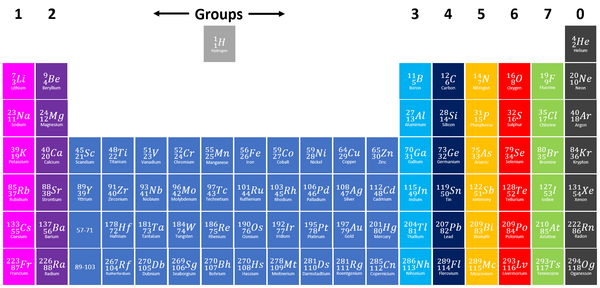
|[[File:PeriodicTableGroups.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:PeriodicTableGroups.png|center|600px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ===Trends within groups=== | |
The [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] of [[element]]s within a '''group''' are similar. However, the [[reactivity]] within a '''group''' changes as you move up or down the [[Period (Chemistry)|period]]s. | The [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] of [[element]]s within a '''group''' are similar. However, the [[reactivity]] within a '''group''' changes as you move up or down the [[Period (Chemistry)|period]]s. | ||
*[[Group 1]]: The [[Alkali Metal]]s all react strongly with water. The [[reactivity]] increases as you go down the '''group'''. | *[[Group 1]]: The [[Alkali Metal]]s all react strongly with water. The [[reactivity]] increases as you go down the '''group'''. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
The [[Physical Property|physical properties]] of [[element]]s within a '''group''' are similar. However, the property changes gradually as you move down the '''group'''. | The [[Physical Property|physical properties]] of [[element]]s within a '''group''' are similar. However, the property changes gradually as you move down the '''group'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | A '''Group''' is a column on the [[Periodic Table]] with [[element]]s with the same number of [[electron]]s on the [[Outer Shell]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Groups=== | ||
| + | : [[Helium]], in [[Group 0]] is an exception to this rule as it has 2 [[electron]]s in its [[Outer Shell]]. | ||
| + | : The [[element]]s were oringally arranged '''groups''' of similar [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]]. | ||
| + | : It was later discovered that [[element]]s have similar [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] when they have the same number of [[electron]]s in their [[Outer Shell]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:PeriodicTableGroups.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ===Trends within groups=== | ||
| + | The [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] of [[element]]s within a '''group''' are similar. However, the [[reactivity]] within a '''group''' changes as you move up or down the [[Period (Chemistry)|period]]s due to the number of [[Electron Shell]]s. | ||
| + | ====[[Group 1]]: The [[Alkali Metal]]==== | ||
| + | =====Chemical Properties===== | ||
| + | : '''Alkali Metals''' are all highly [[Reactivity|reactive]] and will [[Oxidation|oxidise]] quickly in the presence of [[Oxygen]]. | ||
| + | : '''Alkali Metals''' all [[Chemical Reaction|react]] strongly with [[water]] to produce [[Metal Hydroxide|metal hydroxides]] and [[Hydrogen]] [[gas]]. | ||
| + | : '''Alkali Metals''' all produce strong [[alkali]]s. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
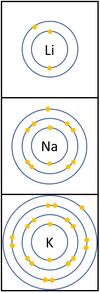
| + | |[[File:Group1ElectronShells.png|center|100px]] | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:left;" |In a [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] the [[electron]] in the [[Outer Shell|outer shell]] is lost. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[reactivity]] increases as you go down the group because: | ||
| + | *The outer [[electron]] is further away from the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] with each additional [[Electron Orbital|electron shell]] making the [[force]] of [[attract]]ion weaker. This makes it easier for an [[atom]] to lose it's outer [[electron]]. | ||
| + | *Even though the [[Electrical Charge|charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] increases the outer [[electron]] is shielded from most of the [[Positive Charge|positive charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] by [[electron]]s in the inner shells. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | =====Physical Properties===== | ||
| + | : '''Alkali Metals''' have a low [[density]] compared to other [[metal]]s. | ||
| + | : '''Alkali Metals''' are all [[solid]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]] but have a low [[Melting Point|melting point]] compared to other [[metal]]s. | ||
| + | : '''Alkali Metals''' are soft and can be easily cut. | ||
| + | : '''Alkali Metals''' all appear shiny (before they [[oxidation|oxidise]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====[[Group 7]]: The [[Halogen]]s==== | ||
| + | =====Chemical Properties===== | ||
| + | : The [[reactivity]] of '''Halogens''' decreases as you go down the [[Periodic Table]]. | ||
| + | : '''Halogens''' all [[Chemical Reaction|react]] strongly as [[Bleaching Agent|bleaching agents]]. | ||
| + | : '''Halogens''' all produce [[acid]]s when combined with [[Hydrogen]]. | ||
| + | : '''Halogens''' are [[toxic]] to [[bacteria]] and are used in [[disinfectant]]s. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
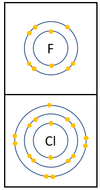
| + | |[[File:Group7ElectronShells.png|center|100px]] | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:left;" |In a [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] an extra [[electron]] is added to the [[Outer Shell|outer shell]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[reactivity]] decreases as you go down the group because: | ||
| + | *The outer [[electron]]s are further away from the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] with each additional [[Electron Orbital|electron shell]] making the [[force]] of [[attract]]ion weaker. This makes it less able to gain an extra [[electron]]. | ||
| + | *Even though the [[Electrical Charge|charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] increases the outer [[electron]]s are shielded from most of the [[Positive Charge|positive charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] by [[electron]]s in the inner shells. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | =====Physical Properties===== | ||
| + | The [[Physical Property|physical properties]] of '''Halogens''' changes significantly as you go down the [[Periodic Table]]: | ||
| + | *[[Fluorine]] - A yellow [[gas]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]]. | ||
| + | *[[Chlorine]] - A green [[gas]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]]. | ||
| + | *[[Bromine]] - A brown [[liquid]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]]. | ||
| + | *[[Iodine]] - A purple [[solid]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]]. | ||
| + | *[[Astatine]] -A dark purple [[solid]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]]. | ||
| + | : The [[density]], [[Melting Point|melting point]] and [[Boiling Point|boiling point]] all increase as you go down the [[Periodic Table]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====[[Group 0]]: The [[Noble Gases]]==== | ||
| + | =====Chemical Properties===== | ||
| + | : The '''Nobel Gases''' are all [[inert]] (unreactive) because they have a full [[Outer Shell|outer shell]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Physical Properties===== | ||
| + | : The '''Nobel Gases''' are all [[gas]]es at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]]. | ||
| + | : The [[density]] and [[Boiling Point|boiling point]] all increase as you go down the [[Periodic Table]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Groups (of the periodic table), page 173, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Groups (of the periodic table), page 29, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Groups (of the periodic table); group 0 elements, pages 134-135, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Groups (of the periodic table); group 0 elements, pages 248-249, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Groups (of the periodic table); group 1 elements, pages 128-129, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Groups (of the periodic table); group 1 elements, pages 242-243, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Groups (of the periodic table); group 7 elements, pages 130-131, 132-133, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Groups (of the periodic table); group 7 elements, pages 244-245, 246-247, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Groups (of the periodic table); valency, page 185, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Groups (of the periodic table); valency, page 41, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Groups (periodic table), pages 81-83, 123, 124, 126, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Groups, pages 18-20, 73, 74, 76, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Groups (in the periodic table), pages 87-89, 121-125, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Groups, pages 16-18, 51, 52, 54, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:33, 11 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A Group is a column on the Periodic Table with elements with the same number of electrons on the Outer Shell.
About Groups
- Helium, in Group 0 is an exception to this rule as it has 2 electrons in its Outer Shell.
- The elements are arranged groups of similar chemical properties.
- Elements have similar chemical properties when they have the same number of electrons in the Outer Shell.
Trends within groups
The chemical properties of elements within a group are similar. However, the reactivity within a group changes as you move up or down the periods.
- Group 1: The Alkali Metals all react strongly with water. The reactivity increases as you go down the group.
- Group 2: The Alkali Earth Metals all react strongly with steam and acids. The reactivity increases as you go down the group.
- Group 7: The Halogens all act as bleaching agents and kill bacteria. The reactivity decreases as you go down the group.
- Group 0: The Noble Gases are all inert (unreactive).
The physical properties of elements within a group are similar. However, the property changes gradually as you move down the group.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A Group is a column on the Periodic Table with elements with the same number of electrons on the Outer Shell.
About Groups
- Helium, in Group 0 is an exception to this rule as it has 2 electrons in its Outer Shell.
- The elements were oringally arranged groups of similar chemical properties.
- It was later discovered that elements have similar chemical properties when they have the same number of electrons in their Outer Shells.
Trends within groups
The chemical properties of elements within a group are similar. However, the reactivity within a group changes as you move up or down the periods due to the number of Electron Shells.
Group 1: The Alkali Metal
Chemical Properties
- Alkali Metals are all highly reactive and will oxidise quickly in the presence of Oxygen.
- Alkali Metals all react strongly with water to produce metal hydroxides and Hydrogen gas.
- Alkali Metals all produce strong alkalis.
| In a chemical reaction the electron in the outer shell is lost.
The reactivity increases as you go down the group because:
|
Physical Properties
- Alkali Metals have a low density compared to other metals.
- Alkali Metals are all solid at room temperature but have a low melting point compared to other metals.
- Alkali Metals are soft and can be easily cut.
- Alkali Metals all appear shiny (before they oxidise).
Group 7: The Halogens
Chemical Properties
- The reactivity of Halogens decreases as you go down the Periodic Table.
- Halogens all react strongly as bleaching agents.
- Halogens all produce acids when combined with Hydrogen.
- Halogens are toxic to bacteria and are used in disinfectants.
| In a chemical reaction an extra electron is added to the outer shell.
The reactivity decreases as you go down the group because:
|
Physical Properties
The physical properties of Halogens changes significantly as you go down the Periodic Table:
- Fluorine - A yellow gas at room temperature.
- Chlorine - A green gas at room temperature.
- Bromine - A brown liquid at room temperature.
- Iodine - A purple solid at room temperature.
- Astatine -A dark purple solid at room temperature.
- The density, melting point and boiling point all increase as you go down the Periodic Table.
Group 0: The Noble Gases
Chemical Properties
- The Nobel Gases are all inert (unreactive) because they have a full outer shell.
Physical Properties
- The Nobel Gases are all gases at room temperature.
- The density and boiling point all increase as you go down the Periodic Table.
References
Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table), page 173, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table), page 29, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 0 elements, pages 134-135, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 0 elements, pages 248-249, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 1 elements, pages 128-129, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 1 elements, pages 242-243, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 7 elements, pages 130-131, 132-133, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 7 elements, pages 244-245, 246-247, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); valency, page 185, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); valency, page 41, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (periodic table), pages 81-83, 123, 124, 126, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Groups, pages 18-20, 73, 74, 76, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel